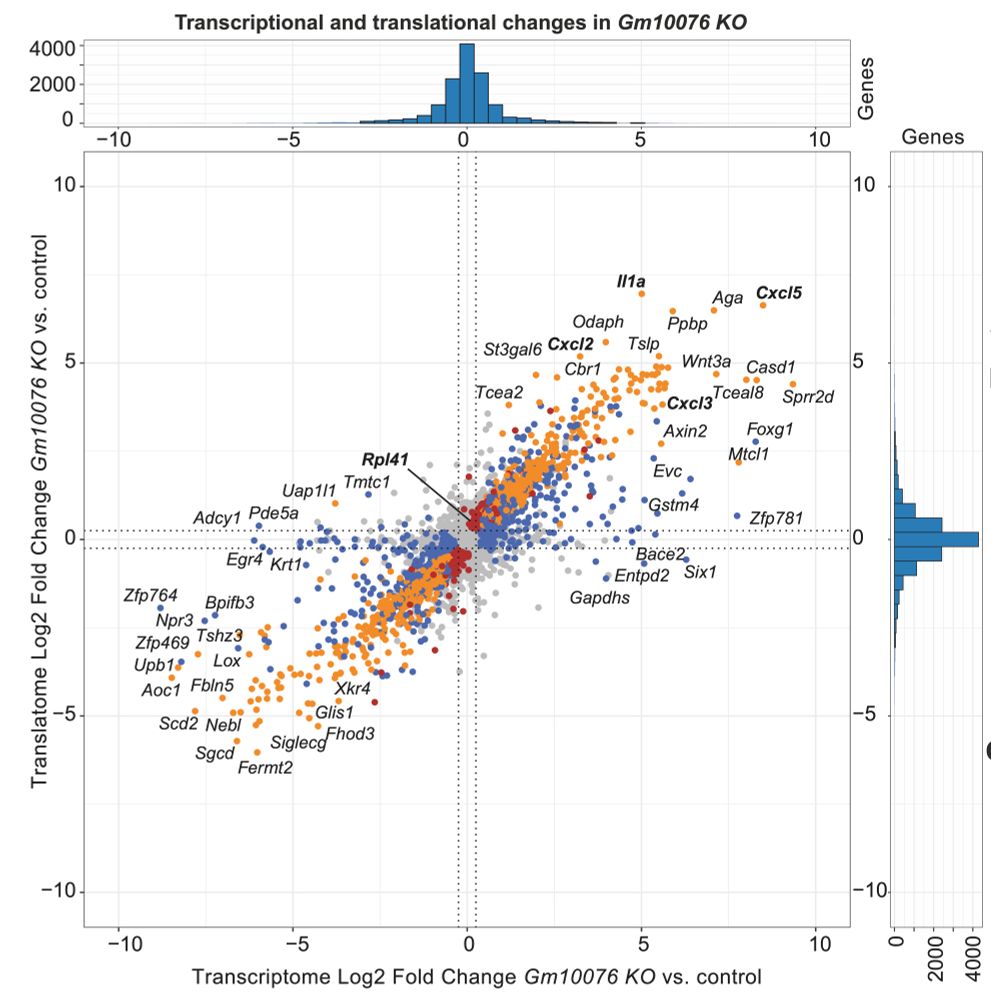
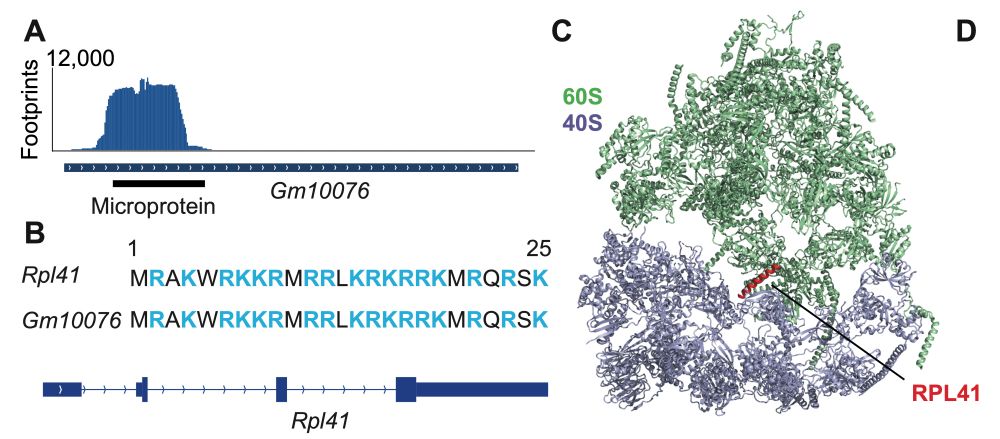
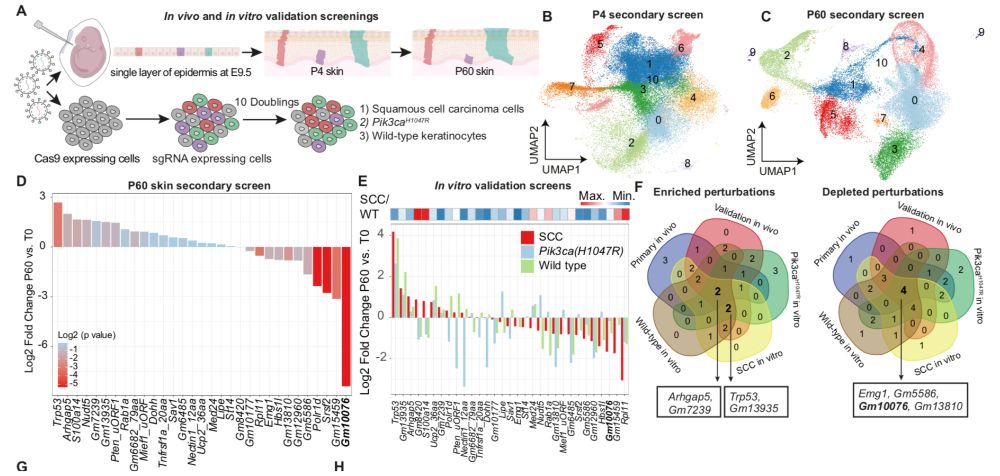
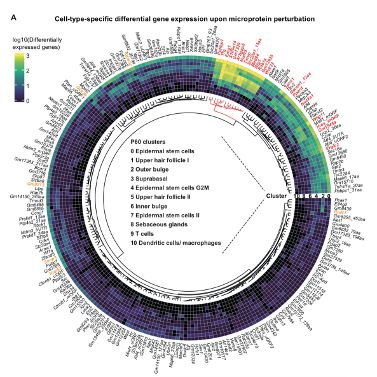
We are excited about mRNA translation, stem cells and cancer.
www.sendoellab.org



Wishing you all the best in your next chapters, we’re excited to see what comes next for you!

Wishing you all the best in your next chapters, we’re excited to see what comes next for you!









www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...