
Acrosome: Contains hydrolytic enzymes.
Nucleus: Holding DNA.
Centriole: Forming the axoneme.
Mitochondria: Generate ATP for movement.
Axoneme: Propels the sperm cell.
Acrosome: Contains hydrolytic enzymes.
Nucleus: Holding DNA.
Centriole: Forming the axoneme.
Mitochondria: Generate ATP for movement.
Axoneme: Propels the sperm cell.

After bringing up my pet peeve - left-handed DNA - in my Halloween video, I want to pivot to a quick rant about the real shape of mitochondria.
After bringing up my pet peeve - left-handed DNA - in my Halloween video, I want to pivot to a quick rant about the real shape of mitochondria.
The red forms the central pore through which Ca++ ions pass.
The extracellular and intracellular proteins regulate channel activation and inactivation.

The red forms the central pore through which Ca++ ions pass.
The extracellular and intracellular proteins regulate channel activation and inactivation.
And yes, I'm well aware of Z-DNA. But that's not an excuse if you don't have a zig-zag backbone. Speaking of the backbone, why didn't I use "spinal cord" there? Ugh!
Anyway, happy Halloween!
And yes, I'm well aware of Z-DNA. But that's not an excuse if you don't have a zig-zag backbone. Speaking of the backbone, why didn't I use "spinal cord" there? Ugh!
Anyway, happy Halloween!

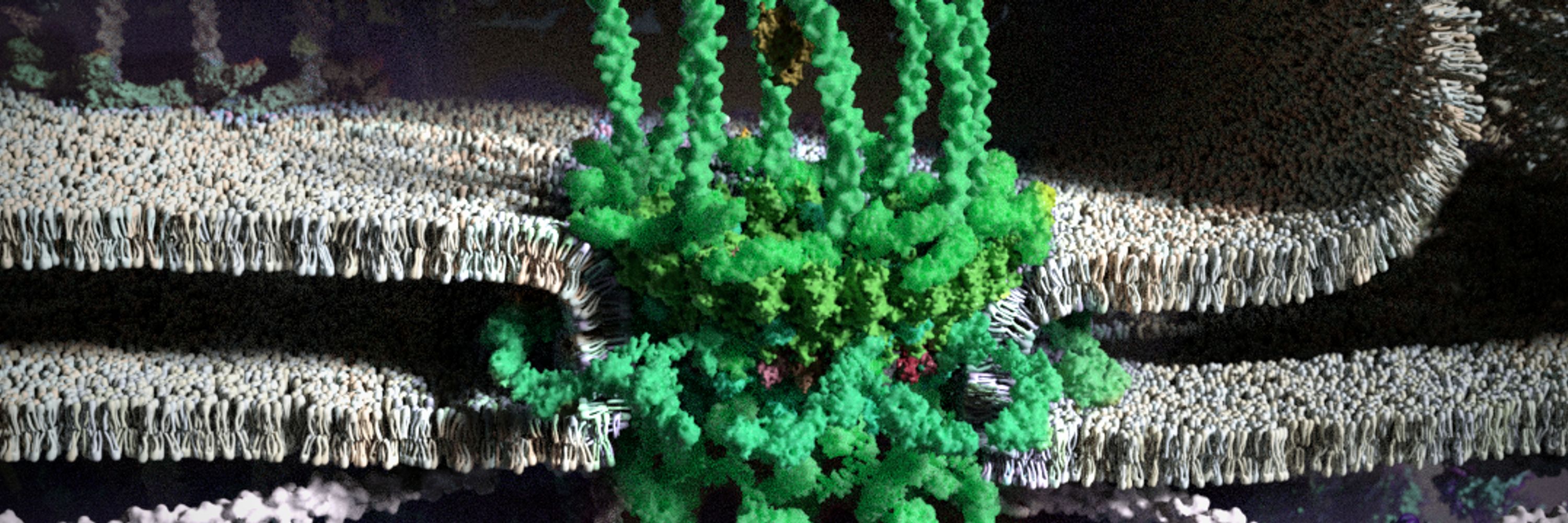
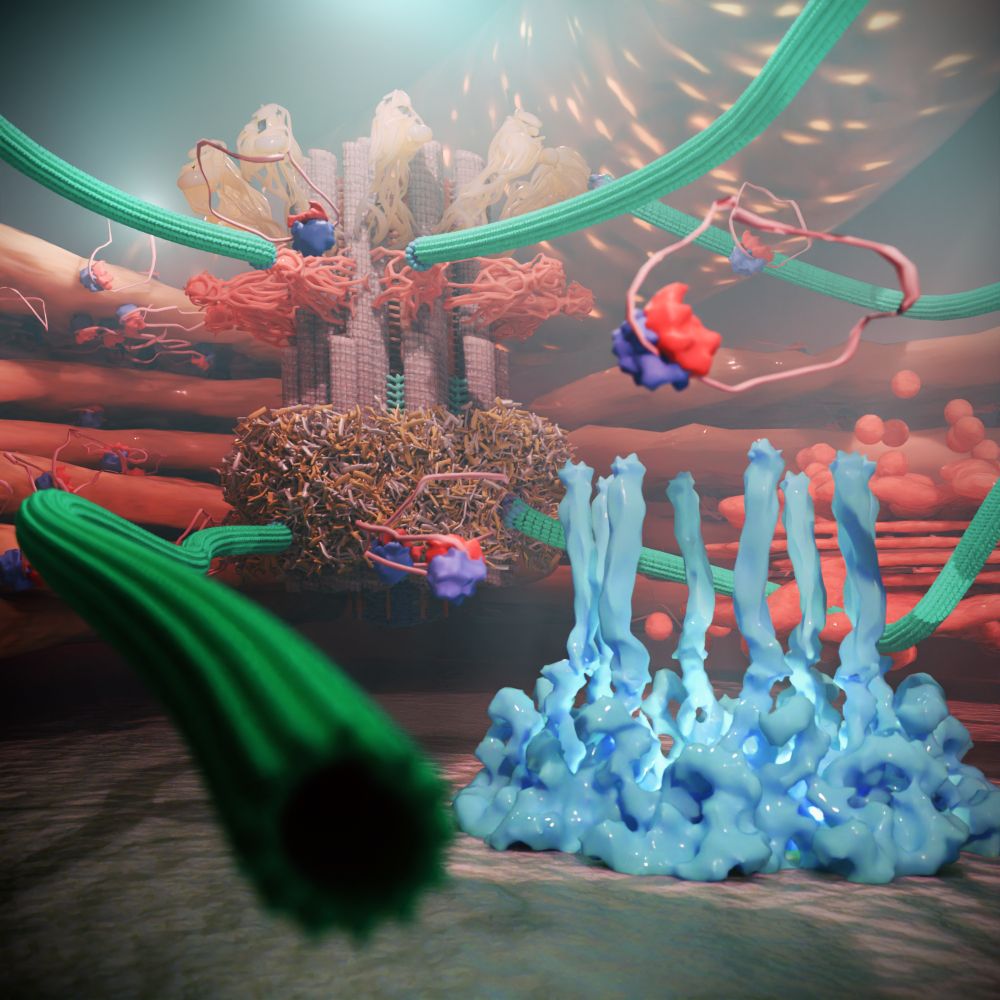
The V-ATPase maintains an electrochemical gradient, which the VAChT uses to load the vesicle with acetylcholine. Synaptobrevin teams up with Syntaxin and SNAP-25 on the membrane.

The V-ATPase maintains an electrochemical gradient, which the VAChT uses to load the vesicle with acetylcholine. Synaptobrevin teams up with Syntaxin and SNAP-25 on the membrane.

