➡️ As I (very roughly) calculate, the German subsidy won’t dramatically undercut competitors - because German prices are high to start with. (10/23)
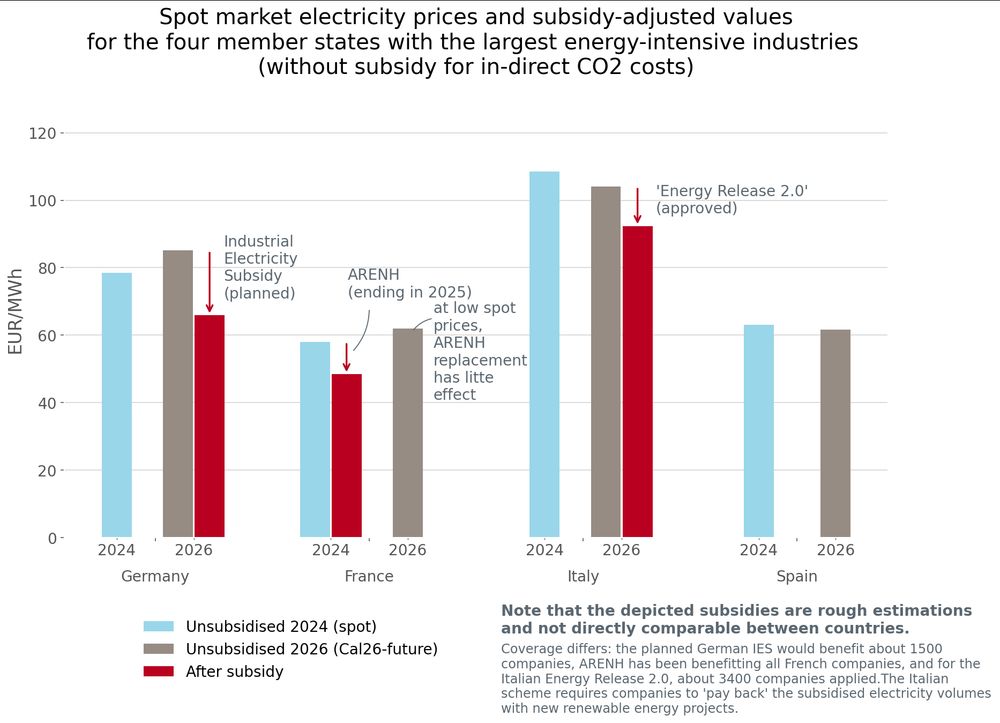
➡️ As I (very roughly) calculate, the German subsidy won’t dramatically undercut competitors - because German prices are high to start with. (10/23)
Note that Germany, and other MS, offer big subsidies on taxes&levies. Companies eligible for the IES pay almost nothing for those in Germany (especially compared to households). (8/23)
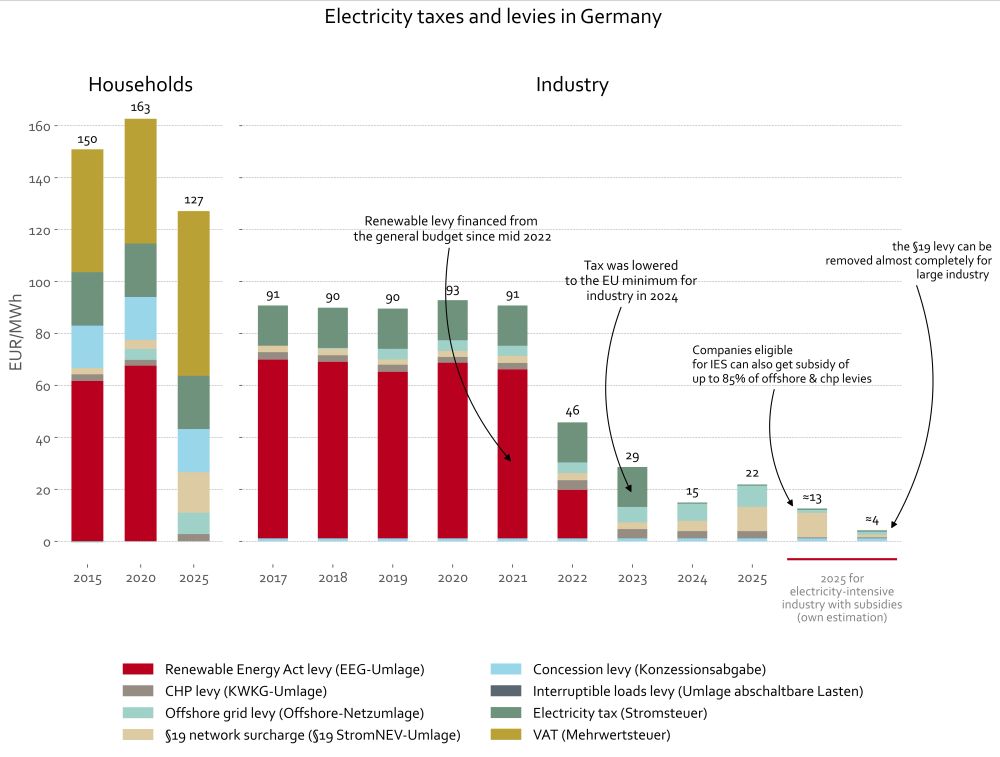
Note that Germany, and other MS, offer big subsidies on taxes&levies. Companies eligible for the IES pay almost nothing for those in Germany (especially compared to households). (8/23)
You can play around with the assumptions for all EU countries here: delors-data.eu/IES/
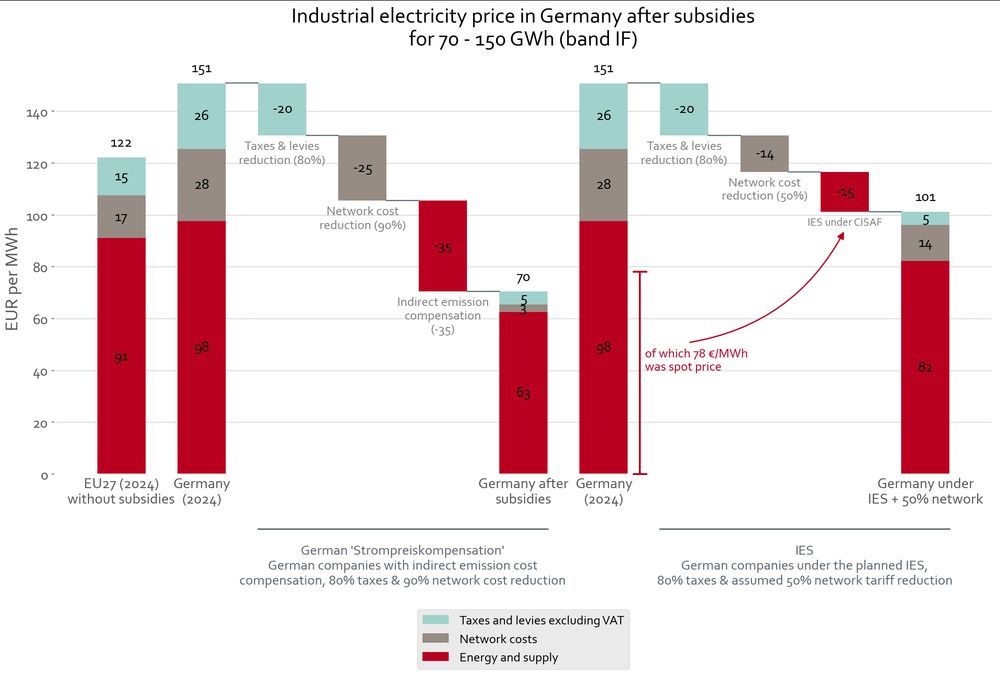
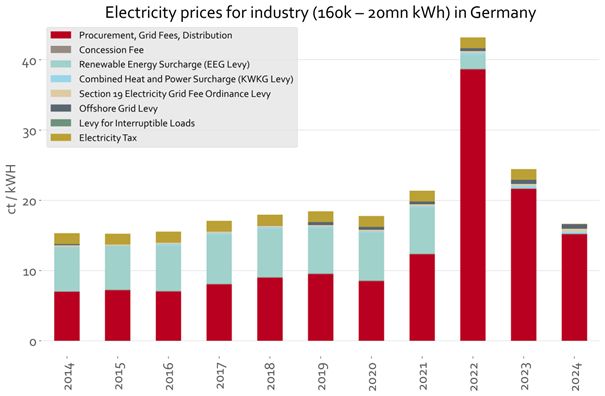
The chart below shows it for Germany. (7/23)

You can play around with the assumptions for all EU countries here: delors-data.eu/IES/
The chart below shows it for Germany. (7/23)
➡️ Energy- and trade-intensive sectors. But some of these can already get another subsidy the (often massive) indirect emission cost compensation - companies can de-facto only get either/or. In DE, this other subsidy is called "Strompreiskompensation" (6/23)
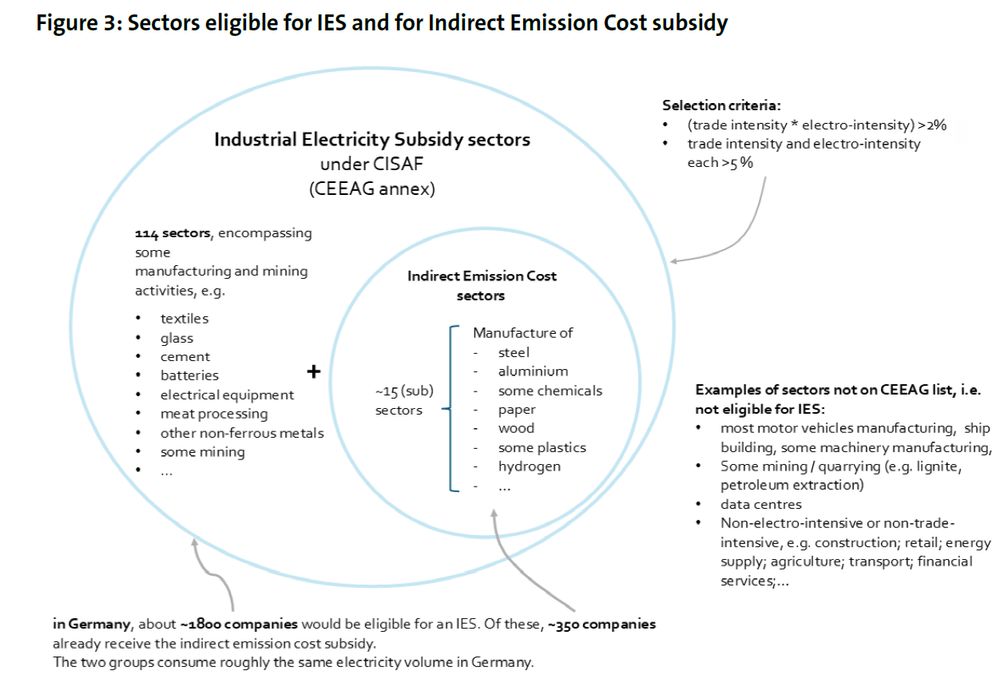
➡️ Energy- and trade-intensive sectors. But some of these can already get another subsidy the (often massive) indirect emission cost compensation - companies can de-facto only get either/or. In DE, this other subsidy is called "Strompreiskompensation" (6/23)
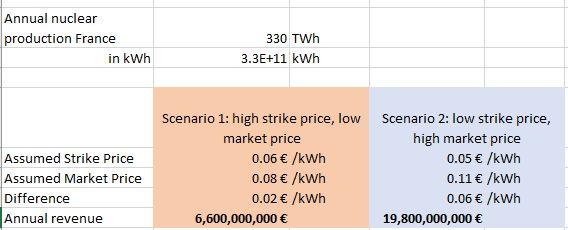
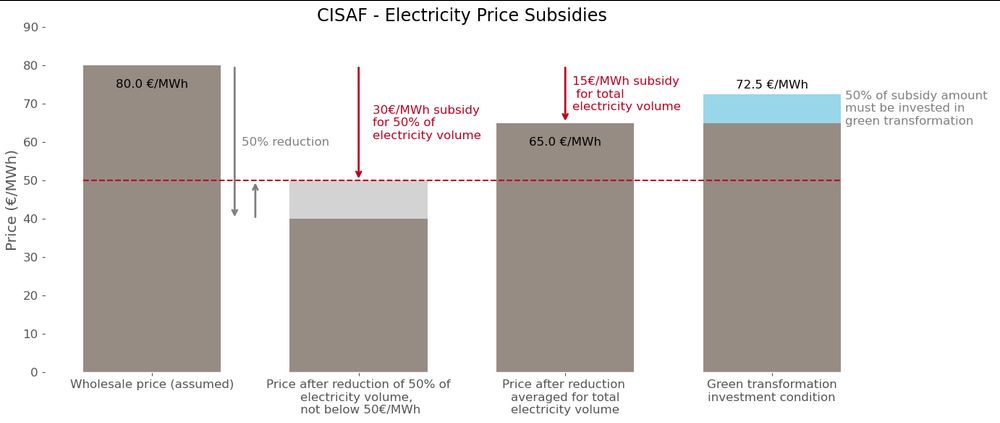
➡️ It depends on the country's wholesale prices. For Germany, at wholesale prices of ~80€/MWh, the maximum subsidy would be about ~15€/MWh. (5/23)

➡️ It depends on the country's wholesale prices. For Germany, at wholesale prices of ~80€/MWh, the maximum subsidy would be about ~15€/MWh. (5/23)
On clean tech, Chinese products are often MUCH cheaper. And EU-based producers continue to lose market share in the EU and globally. The chart shows the recent developments (higher quality in PDF): (5/n)
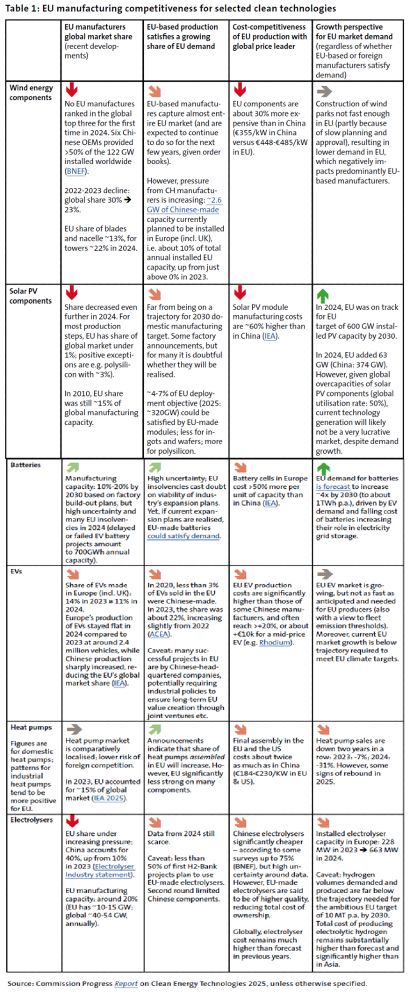
On clean tech, Chinese products are often MUCH cheaper. And EU-based producers continue to lose market share in the EU and globally. The chart shows the recent developments (higher quality in PDF): (5/n)
The chart shows how previous EU sectoral policy relates to the CID, and what legislation to expect: (4/n)
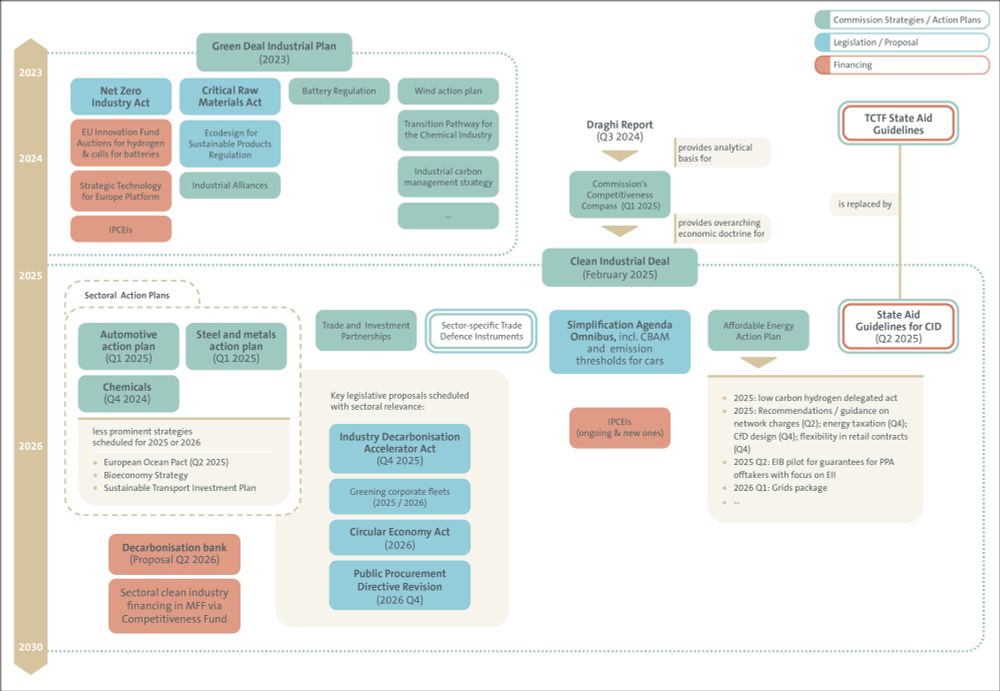
The chart shows how previous EU sectoral policy relates to the CID, and what legislation to expect: (4/n)

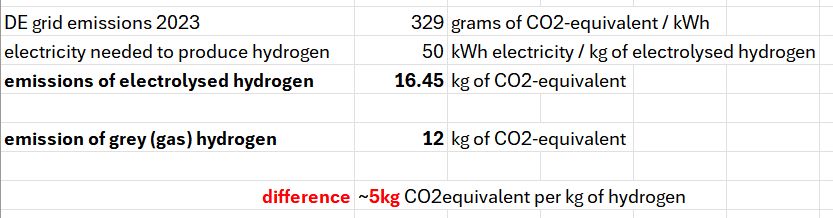


Below the alignment potential of different tools: (9/n)

Below the alignment potential of different tools: (9/n)
Short thread
report: bit.ly/3OD3qHJ

Short thread
report: bit.ly/3OD3qHJ

2) More R&D spending, to catch up with US etc (see chart below). (7/17)

2) More R&D spending, to catch up with US etc (see chart below). (7/17)