language and vision in brains & machines
cognitive science 🤝 AI 🤝 cognitive neuroscience
michaheilbron.github.io
Strikingly these same models that were demonstrably better at the language task, were worse at predicting human reading behaviour
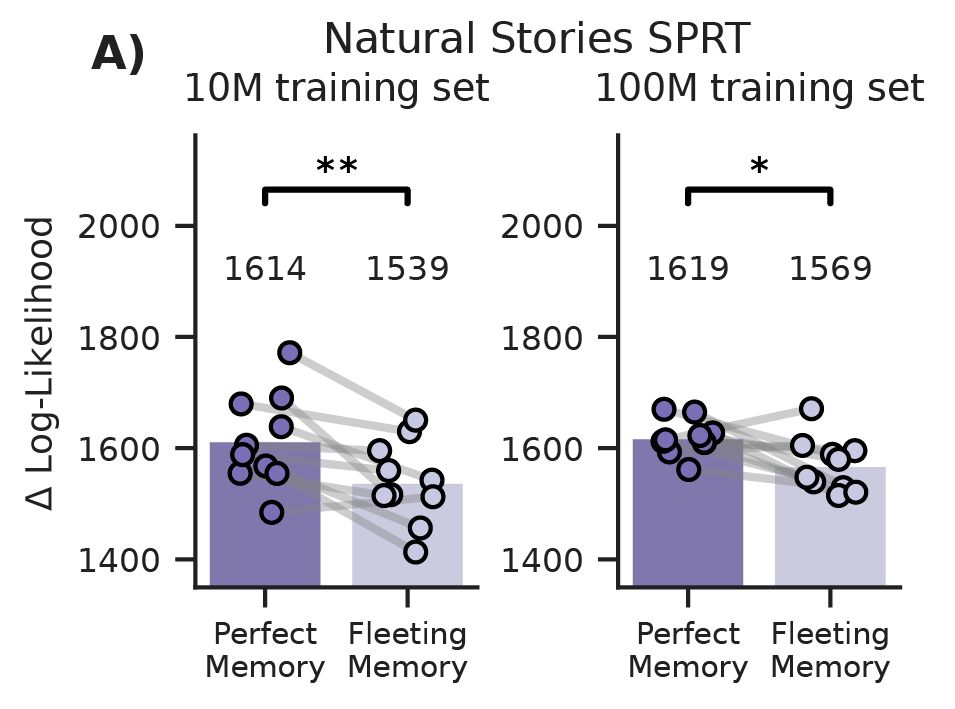
Strikingly these same models that were demonstrably better at the language task, were worse at predicting human reading behaviour
Fleeting memory models achieved better next-token prediction (lower loss) and better syntactic knowledge (higher accuracy) on the BLiMP benchmark
This was consistent across seeds and for both 10M and 100M training sets

Fleeting memory models achieved better next-token prediction (lower loss) and better syntactic knowledge (higher accuracy) on the BLiMP benchmark
This was consistent across seeds and for both 10M and 100M training sets
Human memory has a brief 'echoic' buffer that perfectly preserves the immediate past. When we added this – a short window of perfect retention before the decay -- the pattern flipped
Now, fleeting memory *helped* (lower loss)

Human memory has a brief 'echoic' buffer that perfectly preserves the immediate past. When we added this – a short window of perfect retention before the decay -- the pattern flipped
Now, fleeting memory *helped* (lower loss)

We applied a power-law memory decay to the self-attention scores, simulating how access to past words fades over time, and ran controlled experiments on the developmentally realistic BabyLM corpus

We applied a power-law memory decay to the self-attention scores, simulating how access to past words fades over time, and ran controlled experiments on the developmentally realistic BabyLM corpus
Come find me to meet or catch up
Some highlights from students and collaborators:

Come find me to meet or catch up
Some highlights from students and collaborators:
This suggests they rely on long-term, ingrained priors about the statistical structure of the visual world, rather than on recent exposure to these specific images

This suggests they rely on long-term, ingrained priors about the statistical structure of the visual world, rather than on recent exposure to these specific images
This aligns with hierarchical predictive coding models that postulate that prediction error are computed in superficial layers
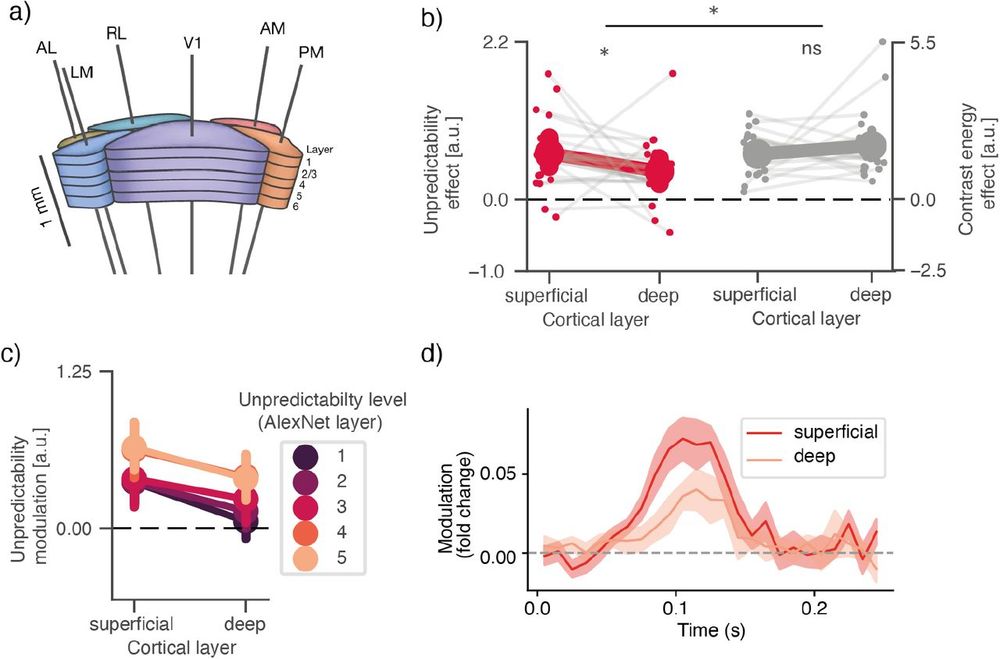
This aligns with hierarchical predictive coding models that postulate that prediction error are computed in superficial layers
Neurons were most sensitive to the *predictability* of high-level visual features (red line), even in areas like V1, most sensitive to low-level visual *features* (blue line)
& this dissociation was found across visual cortex

Neurons were most sensitive to the *predictability* of high-level visual features (red line), even in areas like V1, most sensitive to low-level visual *features* (blue line)
& this dissociation was found across visual cortex
This can dissociate predictability of low-level features (e.g. lines/edges) versus higher-level features (e.g., textures, objects)

This can dissociate predictability of low-level features (e.g. lines/edges) versus higher-level features (e.g., textures, objects)
This aligns with core predictive processing ideas (prediction error) and the established literature using controlled designs (expectation suppression)
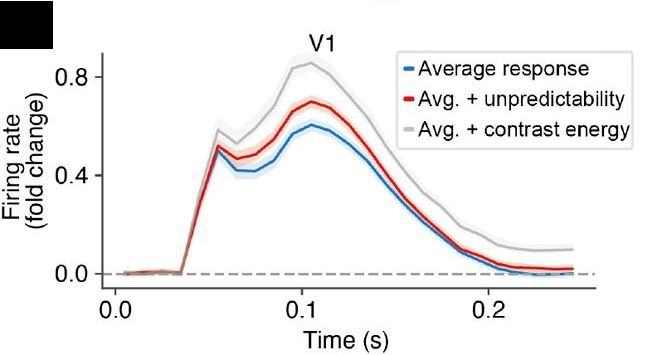
This aligns with core predictive processing ideas (prediction error) and the established literature using controlled designs (expectation suppression)
We then related these scores to spiking from Allen Institute Neuropixels, controlling for low-level features

We then related these scores to spiking from Allen Institute Neuropixels, controlling for low-level features
do reach out if you are around and want to talk language models, brains, or anything in between!

do reach out if you are around and want to talk language models, brains, or anything in between!



For each word in the text, we model how much information (in bits) was available at the previous fixation location, from both prediction — p(word | context) — and preview — P(word | preview)

For each word in the text, we model how much information (in bits) was available at the previous fixation location, from both prediction — p(word | context) — and preview — P(word | preview)




