Matías Goldin
@matigoldin.bsky.social
Neuroscientist @ Institut de la Vision, Paris
Retinal computations and circuits.
Retinal computations and circuits.
13/
Thanks to @tom-quetu.bsky.social, @touchmovelab.bsky.social, and our supporters:
@frm-officiel.bsky.social, @fondationdefrance.bsky.social , @ec.europa.eu, @agencerecherche.bsky.social, @c-brains.bsky.social.
Thanks to @tom-quetu.bsky.social, @touchmovelab.bsky.social, and our supporters:
@frm-officiel.bsky.social, @fondationdefrance.bsky.social , @ec.europa.eu, @agencerecherche.bsky.social, @c-brains.bsky.social.
June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
13/
Thanks to @tom-quetu.bsky.social, @touchmovelab.bsky.social, and our supporters:
@frm-officiel.bsky.social, @fondationdefrance.bsky.social , @ec.europa.eu, @agencerecherche.bsky.social, @c-brains.bsky.social.
Thanks to @tom-quetu.bsky.social, @touchmovelab.bsky.social, and our supporters:
@frm-officiel.bsky.social, @fondationdefrance.bsky.social , @ec.europa.eu, @agencerecherche.bsky.social, @c-brains.bsky.social.
12/
We propose that sweep coding in layer 5a may be related to texture decoding.
The longer integration time makes it possible to combine current sensory inputs with modulatory signals — possibly motor-related — from higher order POm.
We propose that sweep coding in layer 5a may be related to texture decoding.
The longer integration time makes it possible to combine current sensory inputs with modulatory signals — possibly motor-related — from higher order POm.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
12/
We propose that sweep coding in layer 5a may be related to texture decoding.
The longer integration time makes it possible to combine current sensory inputs with modulatory signals — possibly motor-related — from higher order POm.
We propose that sweep coding in layer 5a may be related to texture decoding.
The longer integration time makes it possible to combine current sensory inputs with modulatory signals — possibly motor-related — from higher order POm.
11/
This reveals a new dimension in thalamocortical computation:
🔹 Fine, fast features like sticks are inherited from thalamus
🔸 Broader, global features like sweeps are computed in cortex via temporal integration
This reveals a new dimension in thalamocortical computation:
🔹 Fine, fast features like sticks are inherited from thalamus
🔸 Broader, global features like sweeps are computed in cortex via temporal integration
June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
11/
This reveals a new dimension in thalamocortical computation:
🔹 Fine, fast features like sticks are inherited from thalamus
🔸 Broader, global features like sweeps are computed in cortex via temporal integration
This reveals a new dimension in thalamocortical computation:
🔹 Fine, fast features like sticks are inherited from thalamus
🔸 Broader, global features like sweeps are computed in cortex via temporal integration
10/
So where do sweeps come from?
In layer 5a, we found that sweep-tuned neurons integrate stick inputs from VPM and POm over longer timescales.
So where do sweeps come from?
In layer 5a, we found that sweep-tuned neurons integrate stick inputs from VPM and POm over longer timescales.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
10/
So where do sweeps come from?
In layer 5a, we found that sweep-tuned neurons integrate stick inputs from VPM and POm over longer timescales.
So where do sweeps come from?
In layer 5a, we found that sweep-tuned neurons integrate stick inputs from VPM and POm over longer timescales.
9/
Recordings in VPM and POm showed that both thalamic nuclei primarily encode sticks.
POm adds some diversity, but sweep tuning is not clearly present.
Recordings in VPM and POm showed that both thalamic nuclei primarily encode sticks.
POm adds some diversity, but sweep tuning is not clearly present.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
9/
Recordings in VPM and POm showed that both thalamic nuclei primarily encode sticks.
POm adds some diversity, but sweep tuning is not clearly present.
Recordings in VPM and POm showed that both thalamic nuclei primarily encode sticks.
POm adds some diversity, but sweep tuning is not clearly present.
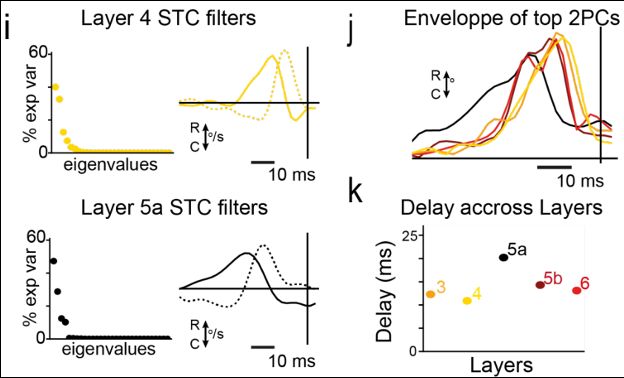
8/
Sticks dominated in layer 4 and 3.
Sweeps were found in layers 5a and 5b.
But can these features be inherited from the thalamus?
Sticks dominated in layer 4 and 3.
Sweeps were found in layers 5a and 5b.
But can these features be inherited from the thalamus?

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
8/
Sticks dominated in layer 4 and 3.
Sweeps were found in layers 5a and 5b.
But can these features be inherited from the thalamus?
Sticks dominated in layer 4 and 3.
Sweeps were found in layers 5a and 5b.
But can these features be inherited from the thalamus?
7/
We identified two distinct types of responses in the cortex:
🔴 Sticks — brief, fast, single-whisker deflections
⚫ Sweeps — broad, multi-whisker movements with large angular changes
These were tuned to perpendicular axes in the feature space.
We identified two distinct types of responses in the cortex:
🔴 Sticks — brief, fast, single-whisker deflections
⚫ Sweeps — broad, multi-whisker movements with large angular changes
These were tuned to perpendicular axes in the feature space.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
7/
We identified two distinct types of responses in the cortex:
🔴 Sticks — brief, fast, single-whisker deflections
⚫ Sweeps — broad, multi-whisker movements with large angular changes
These were tuned to perpendicular axes in the feature space.
We identified two distinct types of responses in the cortex:
🔴 Sticks — brief, fast, single-whisker deflections
⚫ Sweeps — broad, multi-whisker movements with large angular changes
These were tuned to perpendicular axes in the feature space.
6/
We confirmed this with an independent sparse noise stimulus — random single-whisker deflections — and separated the two functional populations.
We confirmed this with an independent sparse noise stimulus — random single-whisker deflections — and separated the two functional populations.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
6/
We confirmed this with an independent sparse noise stimulus — random single-whisker deflections — and separated the two functional populations.
We confirmed this with an independent sparse noise stimulus — random single-whisker deflections — and separated the two functional populations.
5/
But cells were not uniformly selective across this space.
They tended to cluster around two specific feature angles — suggesting a subspace tuning.
But cells were not uniformly selective across this space.
They tended to cluster around two specific feature angles — suggesting a subspace tuning.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
5/
But cells were not uniformly selective across this space.
They tended to cluster around two specific feature angles — suggesting a subspace tuning.
But cells were not uniformly selective across this space.
They tended to cluster around two specific feature angles — suggesting a subspace tuning.
4/
We found that the whisker movements that elicited the strongest responses belonged to a low dimensional feature space.
We could project each cell’s preferred stimulus into this space: the closer to the edge, the more selective.
We found that the whisker movements that elicited the strongest responses belonged to a low dimensional feature space.
We could project each cell’s preferred stimulus into this space: the closer to the edge, the more selective.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
4/
We found that the whisker movements that elicited the strongest responses belonged to a low dimensional feature space.
We could project each cell’s preferred stimulus into this space: the closer to the edge, the more selective.
We found that the whisker movements that elicited the strongest responses belonged to a low dimensional feature space.
We could project each cell’s preferred stimulus into this space: the closer to the edge, the more selective.
3/
Velocity came out on top, as seen in rats (Harrell et al. 2020), and contrary to stick-slip models where velocity and acceleration are encoded equally.
Velocity came out on top, as seen in rats (Harrell et al. 2020), and contrary to stick-slip models where velocity and acceleration are encoded equally.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
3/
Velocity came out on top, as seen in rats (Harrell et al. 2020), and contrary to stick-slip models where velocity and acceleration are encoded equally.
Velocity came out on top, as seen in rats (Harrell et al. 2020), and contrary to stick-slip models where velocity and acceleration are encoded equally.
2/
We designed Gaussian white noise stimuli — optimized to test position, velocity, acceleration — to find which parameter was best encoded by neurons.
We designed Gaussian white noise stimuli — optimized to test position, velocity, acceleration — to find which parameter was best encoded by neurons.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
2/
We designed Gaussian white noise stimuli — optimized to test position, velocity, acceleration — to find which parameter was best encoded by neurons.
We designed Gaussian white noise stimuli — optimized to test position, velocity, acceleration — to find which parameter was best encoded by neurons.
1/
We used a unique setup: 24 whiskers deflected with micrometer precision and millisecond timing.
This allowed us to deliver naturalistic, reproducible input across the full whisker pad, while recording neurons multiple in the barrel cortex.
We used a unique setup: 24 whiskers deflected with micrometer precision and millisecond timing.
This allowed us to deliver naturalistic, reproducible input across the full whisker pad, while recording neurons multiple in the barrel cortex.

June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
1/
We used a unique setup: 24 whiskers deflected with micrometer precision and millisecond timing.
This allowed us to deliver naturalistic, reproducible input across the full whisker pad, while recording neurons multiple in the barrel cortex.
We used a unique setup: 24 whiskers deflected with micrometer precision and millisecond timing.
This allowed us to deliver naturalistic, reproducible input across the full whisker pad, while recording neurons multiple in the barrel cortex.
13/
Thanks to @tom-quetu.bsky.social @touchmovelab.bsky.social , and our supporters:
@frm-officiel.bsky.social , @fondationdefrance.bsky.social , @ec.europa.eu , @agencerecherche.bsky.social , @c-brains.bsky.social
Thanks to @tom-quetu.bsky.social @touchmovelab.bsky.social , and our supporters:
@frm-officiel.bsky.social , @fondationdefrance.bsky.social , @ec.europa.eu , @agencerecherche.bsky.social , @c-brains.bsky.social
June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
13/
Thanks to @tom-quetu.bsky.social @touchmovelab.bsky.social , and our supporters:
@frm-officiel.bsky.social , @fondationdefrance.bsky.social , @ec.europa.eu , @agencerecherche.bsky.social , @c-brains.bsky.social
Thanks to @tom-quetu.bsky.social @touchmovelab.bsky.social , and our supporters:
@frm-officiel.bsky.social , @fondationdefrance.bsky.social , @ec.europa.eu , @agencerecherche.bsky.social , @c-brains.bsky.social
12/
We propose that sweep coding in layer 5a may be related to texture decoding.
The longer integration time makes it possible to combine current sensory inputs with modulatory signals — possibly motor-related — from POm.
We propose that sweep coding in layer 5a may be related to texture decoding.
The longer integration time makes it possible to combine current sensory inputs with modulatory signals — possibly motor-related — from POm.

June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
12/
We propose that sweep coding in layer 5a may be related to texture decoding.
The longer integration time makes it possible to combine current sensory inputs with modulatory signals — possibly motor-related — from POm.
We propose that sweep coding in layer 5a may be related to texture decoding.
The longer integration time makes it possible to combine current sensory inputs with modulatory signals — possibly motor-related — from POm.
11/
This reveals a new dimension in thalamocortical computation:
🔹 Fine, fast features like sticks are inherited from thalamus
🔸 Broader, global features like sweeps are computed in cortex via temporal integration
This reveals a new dimension in thalamocortical computation:
🔹 Fine, fast features like sticks are inherited from thalamus
🔸 Broader, global features like sweeps are computed in cortex via temporal integration
June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
11/
This reveals a new dimension in thalamocortical computation:
🔹 Fine, fast features like sticks are inherited from thalamus
🔸 Broader, global features like sweeps are computed in cortex via temporal integration
This reveals a new dimension in thalamocortical computation:
🔹 Fine, fast features like sticks are inherited from thalamus
🔸 Broader, global features like sweeps are computed in cortex via temporal integration
10/
So where do sweeps come from?
In layer 5a, we found that sweep-tuned neurons integrate stick inputs from VPM and POm over longer timescales — and are probably modulated by POm.
So where do sweeps come from?
In layer 5a, we found that sweep-tuned neurons integrate stick inputs from VPM and POm over longer timescales — and are probably modulated by POm.

June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
10/
So where do sweeps come from?
In layer 5a, we found that sweep-tuned neurons integrate stick inputs from VPM and POm over longer timescales — and are probably modulated by POm.
So where do sweeps come from?
In layer 5a, we found that sweep-tuned neurons integrate stick inputs from VPM and POm over longer timescales — and are probably modulated by POm.
9/
Recordings in VPM and POm showed that both thalamic nuclei primarily encode sticks.
POm adds some diversity, but sweep tuning is not clearly present.
Recordings in VPM and POm showed that both thalamic nuclei primarily encode sticks.
POm adds some diversity, but sweep tuning is not clearly present.

June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
9/
Recordings in VPM and POm showed that both thalamic nuclei primarily encode sticks.
POm adds some diversity, but sweep tuning is not clearly present.
Recordings in VPM and POm showed that both thalamic nuclei primarily encode sticks.
POm adds some diversity, but sweep tuning is not clearly present.
8/
Sticks dominated in layer 4 and 3.
Sweeps were found in layers 5a and 5b.
But can these features be inherited from the thalamus?
Sticks dominated in layer 4 and 3.
Sweeps were found in layers 5a and 5b.
But can these features be inherited from the thalamus?


June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
8/
Sticks dominated in layer 4 and 3.
Sweeps were found in layers 5a and 5b.
But can these features be inherited from the thalamus?
Sticks dominated in layer 4 and 3.
Sweeps were found in layers 5a and 5b.
But can these features be inherited from the thalamus?
7/
We identified two distinct types of responses in cortex:
🔴 Sticks — brief, fast, single-whisker deflections
⚫ Sweeps — broad, multi-whisker movements with large angular changes
These were tuned to perpendicular axes in the feature space.
We identified two distinct types of responses in cortex:
🔴 Sticks — brief, fast, single-whisker deflections
⚫ Sweeps — broad, multi-whisker movements with large angular changes
These were tuned to perpendicular axes in the feature space.

June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
7/
We identified two distinct types of responses in cortex:
🔴 Sticks — brief, fast, single-whisker deflections
⚫ Sweeps — broad, multi-whisker movements with large angular changes
These were tuned to perpendicular axes in the feature space.
We identified two distinct types of responses in cortex:
🔴 Sticks — brief, fast, single-whisker deflections
⚫ Sweeps — broad, multi-whisker movements with large angular changes
These were tuned to perpendicular axes in the feature space.
6/
We confirmed this with an independent sparse noise stimulus — random single-whisker deflections — and separated the two functional populations.
We confirmed this with an independent sparse noise stimulus — random single-whisker deflections — and separated the two functional populations.

June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
6/
We confirmed this with an independent sparse noise stimulus — random single-whisker deflections — and separated the two functional populations.
We confirmed this with an independent sparse noise stimulus — random single-whisker deflections — and separated the two functional populations.
5/
But cells were not uniformly selective across this space.
They tended to cluster around two specific feature angles — suggesting subspace angle tuning.
But cells were not uniformly selective across this space.
They tended to cluster around two specific feature angles — suggesting subspace angle tuning.

June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
5/
But cells were not uniformly selective across this space.
They tended to cluster around two specific feature angles — suggesting subspace angle tuning.
But cells were not uniformly selective across this space.
They tended to cluster around two specific feature angles — suggesting subspace angle tuning.
4/
We found that the whisker movements that elicited the strongest responses belonged to a low dimensional feature space.
We could project each cell’s preferred stimulus into this space: the closer to the edge, the more selective.
We found that the whisker movements that elicited the strongest responses belonged to a low dimensional feature space.
We could project each cell’s preferred stimulus into this space: the closer to the edge, the more selective.

June 12, 2025 at 4:08 PM
4/
We found that the whisker movements that elicited the strongest responses belonged to a low dimensional feature space.
We could project each cell’s preferred stimulus into this space: the closer to the edge, the more selective.
We found that the whisker movements that elicited the strongest responses belonged to a low dimensional feature space.
We could project each cell’s preferred stimulus into this space: the closer to the edge, the more selective.

