
She focused on global RNA-binding proteins in Bacteroides—bacteria lacking Hfq, ProQ, CsrA, Khp—culminating in the discovery of a post-transcriptional network governed by RbpB (www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-55383-8).

She focused on global RNA-binding proteins in Bacteroides—bacteria lacking Hfq, ProQ, CsrA, Khp—culminating in the discovery of a post-transcriptional network governed by RbpB (www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-55383-8).
doi.org/10.1101/2025.09.08.672848

doi.org/10.1101/2025.09.08.672848
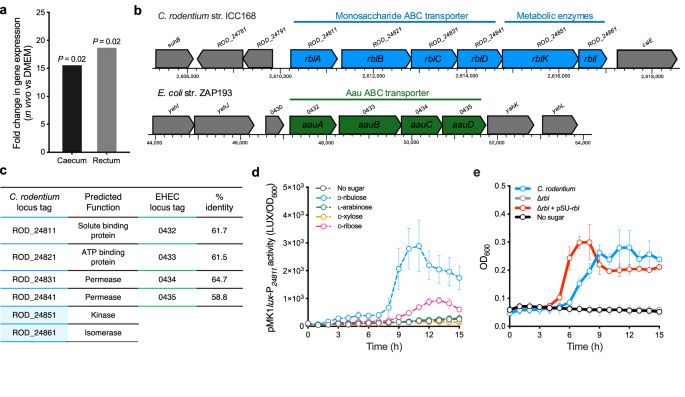
In this study lead by @lenaamend.bsky.social from the group, we explore carbon cross-feeding between a gut commensal and an enteropathogen. Can we counter infection by cutting sugar supply to pathogens?

In this study lead by @lenaamend.bsky.social from the group, we explore carbon cross-feeding between a gut commensal and an enteropathogen. Can we counter infection by cutting sugar supply to pathogens?
Shining a light on these problems is painful for those affected, but is an important step on the long road to reform 🧪
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

Shining a light on these problems is painful for those affected, but is an important step on the long road to reform 🧪
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

We find (>800!) 30S binding sites in hundreds of 5'UTRs, but also new dynamic steps of translation initiation.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Congrats to all co-authors at the RNA control of gene expression lab, IBPC CNRS
(Thread, 1/6)

We find (>800!) 30S binding sites in hundreds of 5'UTRs, but also new dynamic steps of translation initiation.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Congrats to all co-authors at the RNA control of gene expression lab, IBPC CNRS
(Thread, 1/6)
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

