Mastodon: @DebianAstro@fosstodon.org
1/2⤵

1/2⤵

1/5⤵

1/5⤵
1/3⤵

1/3⤵
1/2⤵

1/2⤵
Some core features of Gpredict include:
1/4⤵

Some core features of Gpredict include:
1/4⤵
#AstronomySoftware #Debian

#AstronomySoftware #Debian
Features:
- Stunning visualisations
- Create unlimited variations of simulations
1/3⤵
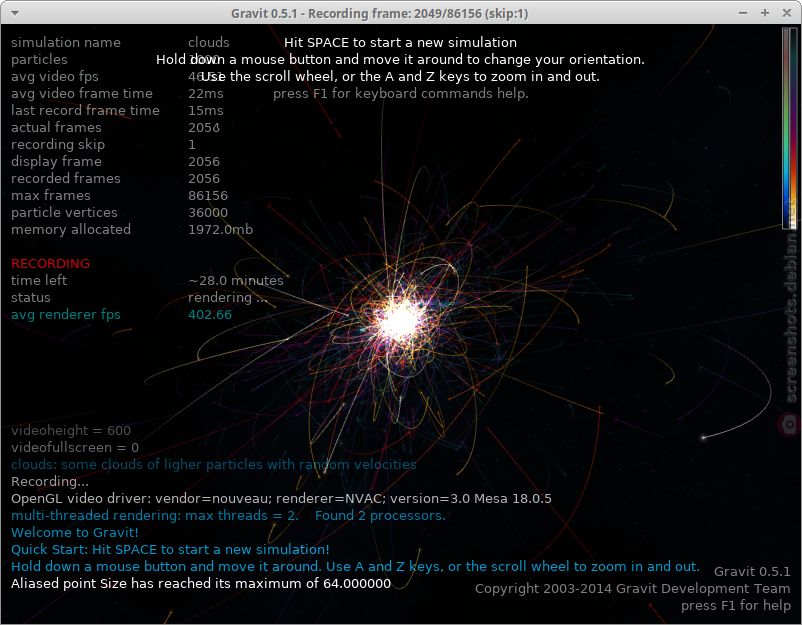
Features:
- Stunning visualisations
- Create unlimited variations of simulations
1/3⤵
Some features:
- default star catalogue with over 600 thousand stars,
1/6⤵

Some features:
- default star catalogue with over 600 thousand stars,
1/6⤵
1/5⤵

1/5⤵
1/2⤵

1/2⤵
1/4⤵

1/4⤵


1/2⤵

1/2⤵
* Visualization of scalar, vector and tensor data in 2 and 3 dimensions
* Easy scriptability using Python
1/4⤵

* Visualization of scalar, vector and tensor data in 2 and 3 dimensions
* Easy scriptability using Python
1/4⤵
Random #Debian Astro package of the week is lynkeos.app. Lynkeos is an application dedicated to the processing of astronomical (mainly planetary) images taken with a webcam through a telescope.
1/2⤵

Random #Debian Astro package of the week is lynkeos.app. Lynkeos is an application dedicated to the processing of astronomical (mainly planetary) images taken with a webcam through a telescope.
1/2⤵
Random #Debian Astro package of the week is splash. This (formerly SUPERSPHPLOT) is a visualisation tool for output from (astrophysical) simulations using the Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) method in one, two and three
1/3⤵

Random #Debian Astro package of the week is splash. This (formerly SUPERSPHPLOT) is a visualisation tool for output from (astrophysical) simulations using the Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) method in one, two and three
1/3⤵
1/2⤵

1/2⤵
1/4⤵

1/4⤵
1/2⤵

1/2⤵
1/4⤵
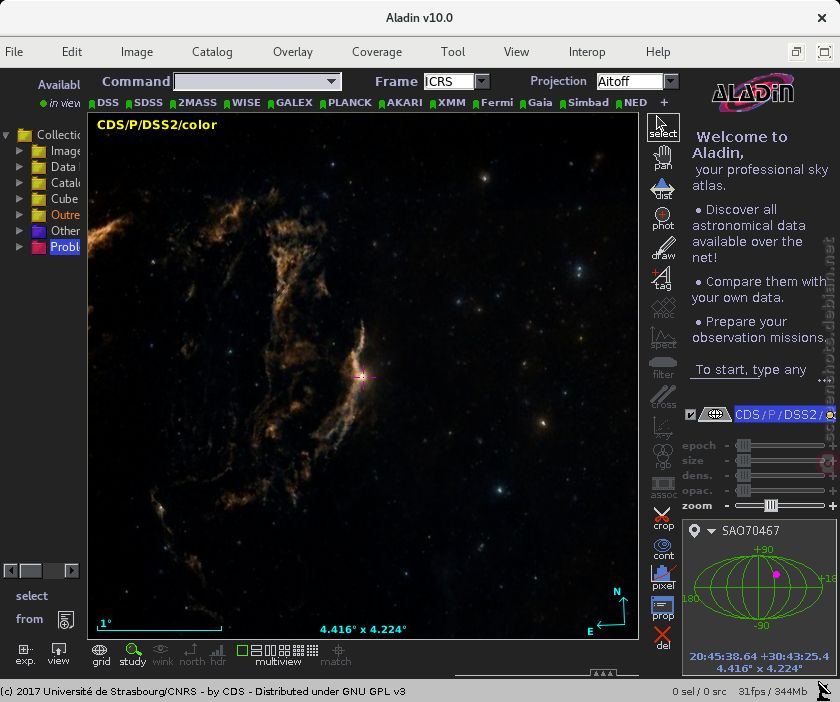
1/4⤵
1/2⤵

1/2⤵


