Chandan Singh
@csinva.bsky.social
Seeking superhuman explanations.
Senior researcher at Microsoft Research, PhD from UC Berkeley, https://csinva.io/
Senior researcher at Microsoft Research, PhD from UC Berkeley, https://csinva.io/
Reposted by Chandan Singh
How can an imitative model like an LLM outperform the experts it is trained on? Our new COLM paper outlines three types of transcendence and shows that each one relies on a different aspect of data diversity. arxiv.org/abs/2508.17669

August 29, 2025 at 9:46 PM
How can an imitative model like an LLM outperform the experts it is trained on? Our new COLM paper outlines three types of transcendence and shows that each one relies on a different aspect of data diversity. arxiv.org/abs/2508.17669
Reposted by Chandan Singh
New paper with @rjantonello.bsky.social @csinva.bsky.social, Suna Guo, Gavin Mischler, Jianfeng Gao, & Nima Mesgarani: We use LLMs to generate VERY interpretable embeddings where each dimension corresponds to a scientific theory, & then use these embeddings to predict fMRI and ECoG. It WORKS!
Evaluating scientific theories as predictive models in language neuroscience https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.08.12.669958v1
August 18, 2025 at 6:34 PM
New paper with @rjantonello.bsky.social @csinva.bsky.social, Suna Guo, Gavin Mischler, Jianfeng Gao, & Nima Mesgarani: We use LLMs to generate VERY interpretable embeddings where each dimension corresponds to a scientific theory, & then use these embeddings to predict fMRI and ECoG. It WORKS!
Reposted by Chandan Singh
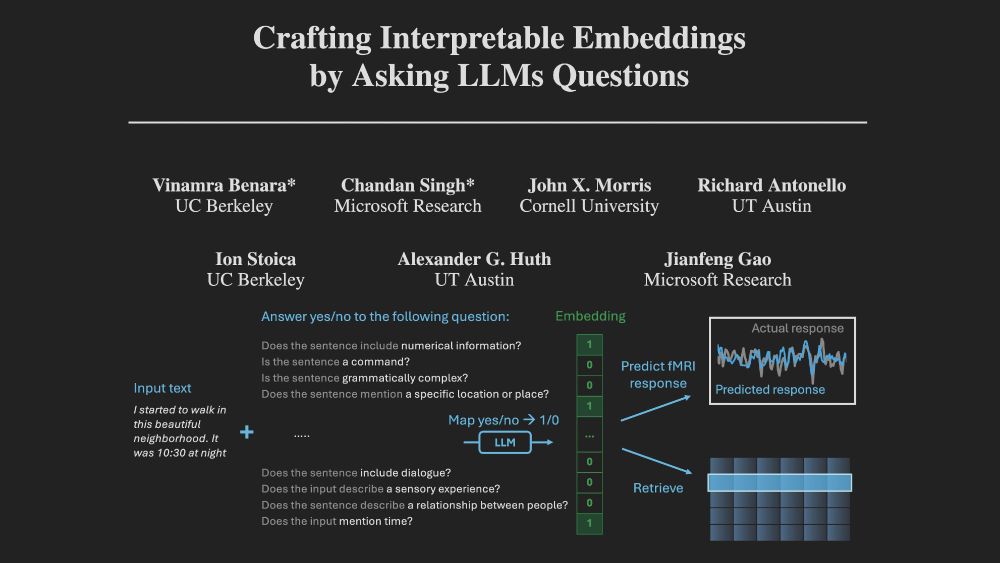
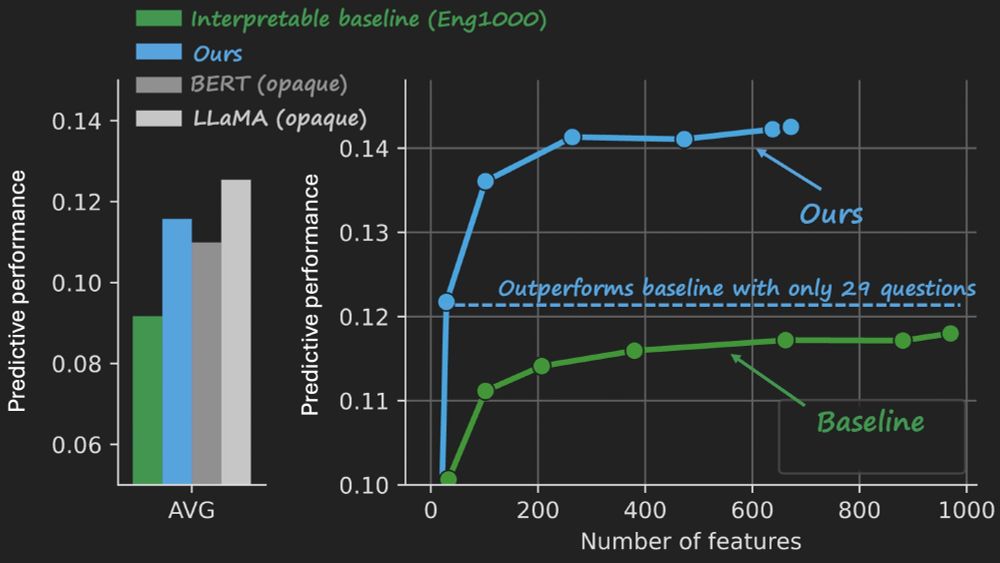
In our new paper, we explore how we can build encoding models that are both powerful and understandable. Our model uses an LLM to answer 35 questions about a sentence's content. The answers linearly contribute to our prediction of how the brain will respond to that sentence. 1/6
August 18, 2025 at 9:42 AM
In our new paper, we explore how we can build encoding models that are both powerful and understandable. Our model uses an LLM to answer 35 questions about a sentence's content. The answers linearly contribute to our prediction of how the brain will respond to that sentence. 1/6
New paper: Ask 35 simple questions about sentences in a story and use the answers to predict brain responses. Interpretable, compact, & surprisingly high performance in both fMRI and ECoG. 🧵 biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

August 14, 2025 at 2:06 PM
New paper: Ask 35 simple questions about sentences in a story and use the answers to predict brain responses. Interpretable, compact, & surprisingly high performance in both fMRI and ECoG. 🧵 biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Reposted by Chandan Singh
We’ve discovered a literal miracle with almost unlimited potential and it’s being scrapped for *no reason whatsoever*. This isn’t even nihilism, it’s outright worship of death and human suffering.
"The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) today announced the beginning of a coordinated wind-down of its mRNA vaccine development activities...."
cc: Sen. Bill Cassidy
cc: Sen. Bill Cassidy

August 5, 2025 at 11:09 PM
We’ve discovered a literal miracle with almost unlimited potential and it’s being scrapped for *no reason whatsoever*. This isn’t even nihilism, it’s outright worship of death and human suffering.
Reposted by Chandan Singh
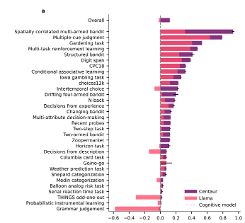
Binz et al. (in press, Nature) developed an LLM called Centaur that better predicts human responses in 159 of 160 behavioural experiments compared to existing cognitive models. See: arxiv.org/abs/2410.20268
June 26, 2025 at 8:29 PM
Binz et al. (in press, Nature) developed an LLM called Centaur that better predicts human responses in 159 of 160 behavioural experiments compared to existing cognitive models. See: arxiv.org/abs/2410.20268
Reposted by Chandan Singh
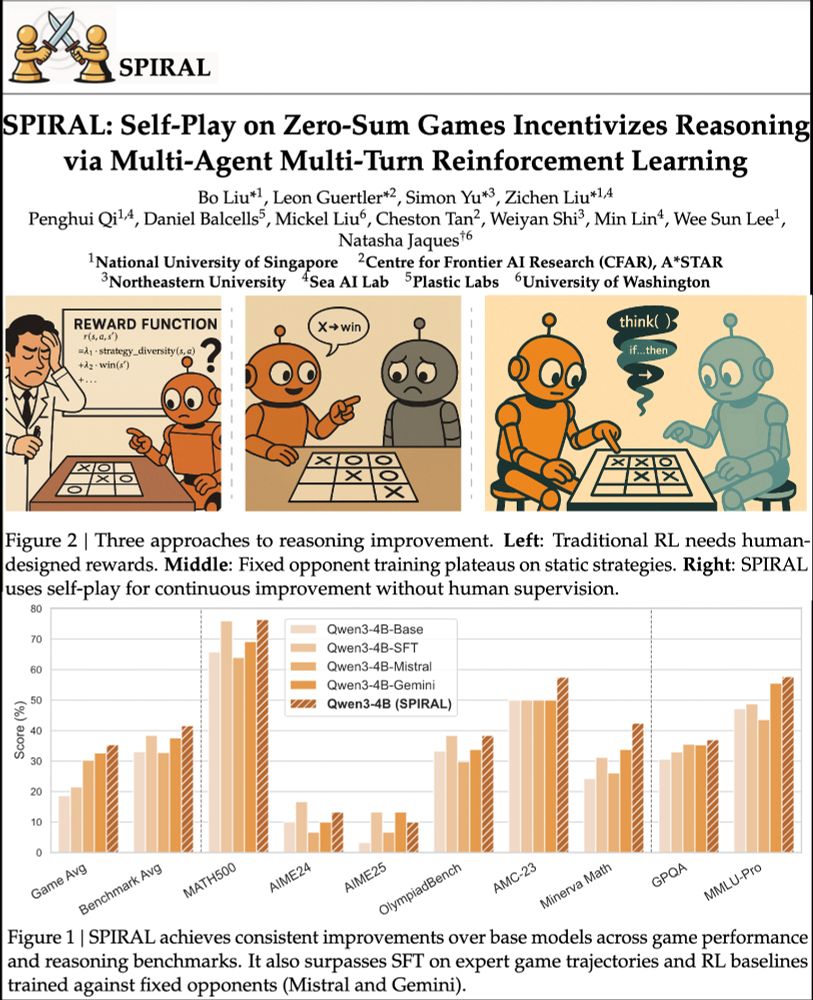
We're excited about self-play unlocking continuously improving agents. RL selects CoT patterns from LLMs. Games=perfect testing grounds.
SPIRAL: models learn via self-competition. Kuhn Poker → +8.7% math, +18.1 Minerva Math! 🃏
Paper: huggingface.co/papers/2506....
Code: github.com/spiral-rl/spiral
SPIRAL: models learn via self-competition. Kuhn Poker → +8.7% math, +18.1 Minerva Math! 🃏
Paper: huggingface.co/papers/2506....
Code: github.com/spiral-rl/spiral
July 1, 2025 at 8:11 PM
We're excited about self-play unlocking continuously improving agents. RL selects CoT patterns from LLMs. Games=perfect testing grounds.
SPIRAL: models learn via self-competition. Kuhn Poker → +8.7% math, +18.1 Minerva Math! 🃏
Paper: huggingface.co/papers/2506....
Code: github.com/spiral-rl/spiral
SPIRAL: models learn via self-competition. Kuhn Poker → +8.7% math, +18.1 Minerva Math! 🃏
Paper: huggingface.co/papers/2506....
Code: github.com/spiral-rl/spiral
Reposted by Chandan Singh
🚨 New preprint 🚨
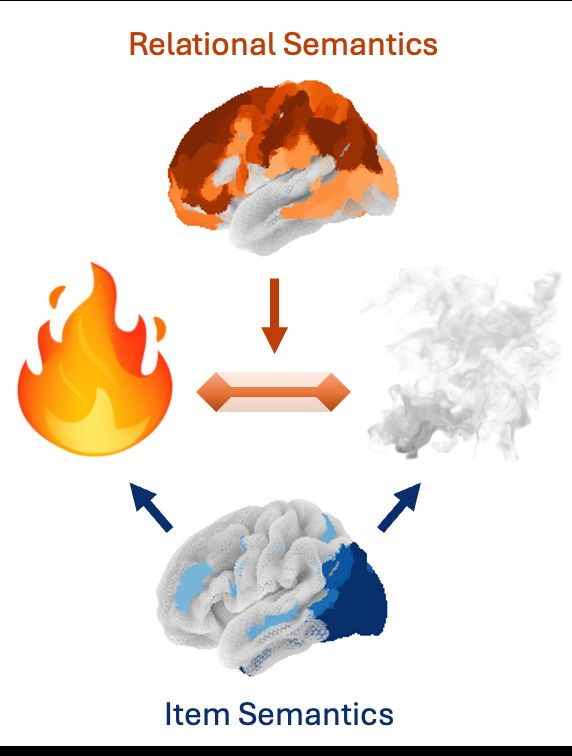
Prior work has mapped how the brain encodes concepts: If you see fire and smoke, your brain will represent the fire (hot, bright) and smoke (gray, airy). But how do you encode features of the fire-smoke relation? We analyzed fMRI with embeddings extracted from LLMs to find out 🧵
Prior work has mapped how the brain encodes concepts: If you see fire and smoke, your brain will represent the fire (hot, bright) and smoke (gray, airy). But how do you encode features of the fire-smoke relation? We analyzed fMRI with embeddings extracted from LLMs to find out 🧵
June 24, 2025 at 1:49 PM
🚨 New preprint 🚨
Prior work has mapped how the brain encodes concepts: If you see fire and smoke, your brain will represent the fire (hot, bright) and smoke (gray, airy). But how do you encode features of the fire-smoke relation? We analyzed fMRI with embeddings extracted from LLMs to find out 🧵
Prior work has mapped how the brain encodes concepts: If you see fire and smoke, your brain will represent the fire (hot, bright) and smoke (gray, airy). But how do you encode features of the fire-smoke relation? We analyzed fMRI with embeddings extracted from LLMs to find out 🧵
Reposted by Chandan Singh
What makes humans similar or different to AI? In a paper out in @natmachintell.nature.com led by @florianmahner.bsky.social & @lukasmut.bsky.social, w/ Umut Güclü, we took a deep look at the factors underlying their representational alignment, with surprising results.
www.nature.com/articles/s42...
www.nature.com/articles/s42...
Dimensions underlying the representational alignment of deep neural networks with humans - Nature Machine Intelligence
An interpretability framework that compares how humans and deep neural networks process images has been presented. Their findings reveal that, unlike humans, deep neural networks focus more on visual ...
www.nature.com
June 23, 2025 at 8:03 PM
What makes humans similar or different to AI? In a paper out in @natmachintell.nature.com led by @florianmahner.bsky.social & @lukasmut.bsky.social, w/ Umut Güclü, we took a deep look at the factors underlying their representational alignment, with surprising results.
www.nature.com/articles/s42...
www.nature.com/articles/s42...
Reposted by Chandan Singh
🚨Paper alert!🚨
TL;DR first: We used a pre-trained deep neural network to model fMRI data and to generate images predicted to elicit a large response for each many different parts of the brain. We aggregate these into an awesome interactive brain viewer: piecesofmind.psyc.unr.edu/activation_m...
TL;DR first: We used a pre-trained deep neural network to model fMRI data and to generate images predicted to elicit a large response for each many different parts of the brain. We aggregate these into an awesome interactive brain viewer: piecesofmind.psyc.unr.edu/activation_m...
Cortex Feature Visualization
piecesofmind.psyc.unr.edu
June 12, 2025 at 4:34 PM
🚨Paper alert!🚨
TL;DR first: We used a pre-trained deep neural network to model fMRI data and to generate images predicted to elicit a large response for each many different parts of the brain. We aggregate these into an awesome interactive brain viewer: piecesofmind.psyc.unr.edu/activation_m...
TL;DR first: We used a pre-trained deep neural network to model fMRI data and to generate images predicted to elicit a large response for each many different parts of the brain. We aggregate these into an awesome interactive brain viewer: piecesofmind.psyc.unr.edu/activation_m...
Reposted by Chandan Singh
What are the organizing dimensions of language processing?
We show that voxel responses during comprehension are organized along 2 main axes: processing difficulty & meaning abstractness—revealing an interpretable, topographic representational basis for language processing shared across individuals
We show that voxel responses during comprehension are organized along 2 main axes: processing difficulty & meaning abstractness—revealing an interpretable, topographic representational basis for language processing shared across individuals
May 23, 2025 at 5:00 PM
What are the organizing dimensions of language processing?
We show that voxel responses during comprehension are organized along 2 main axes: processing difficulty & meaning abstractness—revealing an interpretable, topographic representational basis for language processing shared across individuals
We show that voxel responses during comprehension are organized along 2 main axes: processing difficulty & meaning abstractness—revealing an interpretable, topographic representational basis for language processing shared across individuals
Reposted by Chandan Singh
When it comes to text prediction, where does one LM outperform another? If you've ever worked on LM evals, you know this question is a lot more complex than it seems. In our new #acl2025 paper, we developed a method to find fine-grained differences between LMs:
🧵1/9
🧵1/9
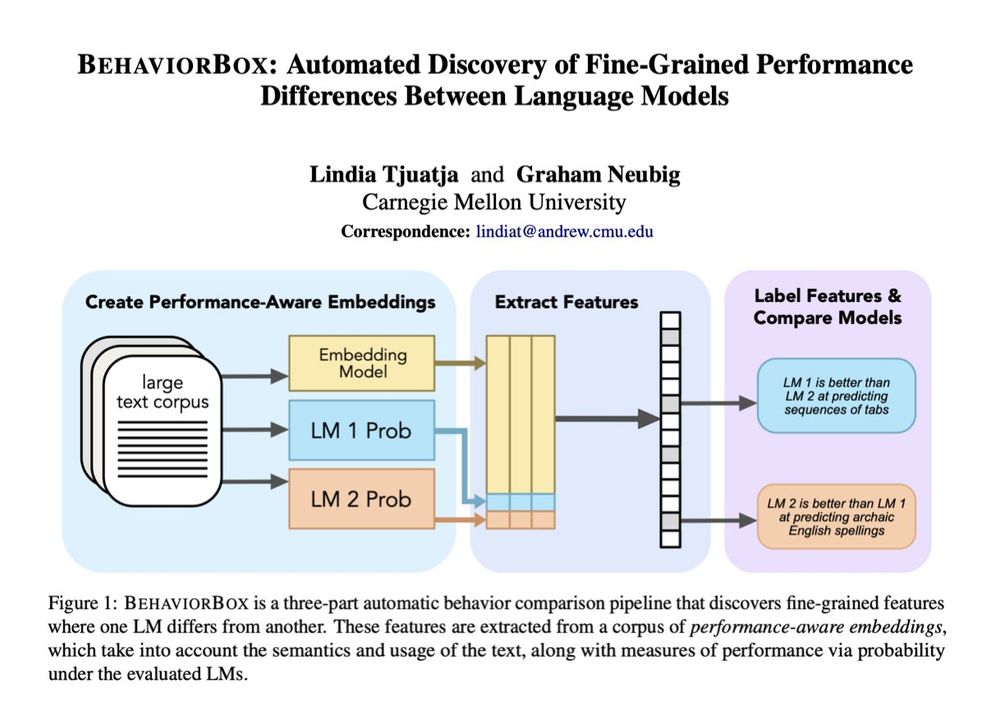
June 9, 2025 at 1:47 PM
When it comes to text prediction, where does one LM outperform another? If you've ever worked on LM evals, you know this question is a lot more complex than it seems. In our new #acl2025 paper, we developed a method to find fine-grained differences between LMs:
🧵1/9
🧵1/9
Reposted by Chandan Singh
Five people have seen a color never before visible to the naked human eye, thanks to a new retinal stimulation technique called Oz.
Learn more in #ScienceAdvances: scim.ag/442Hjn6
Learn more in #ScienceAdvances: scim.ag/442Hjn6
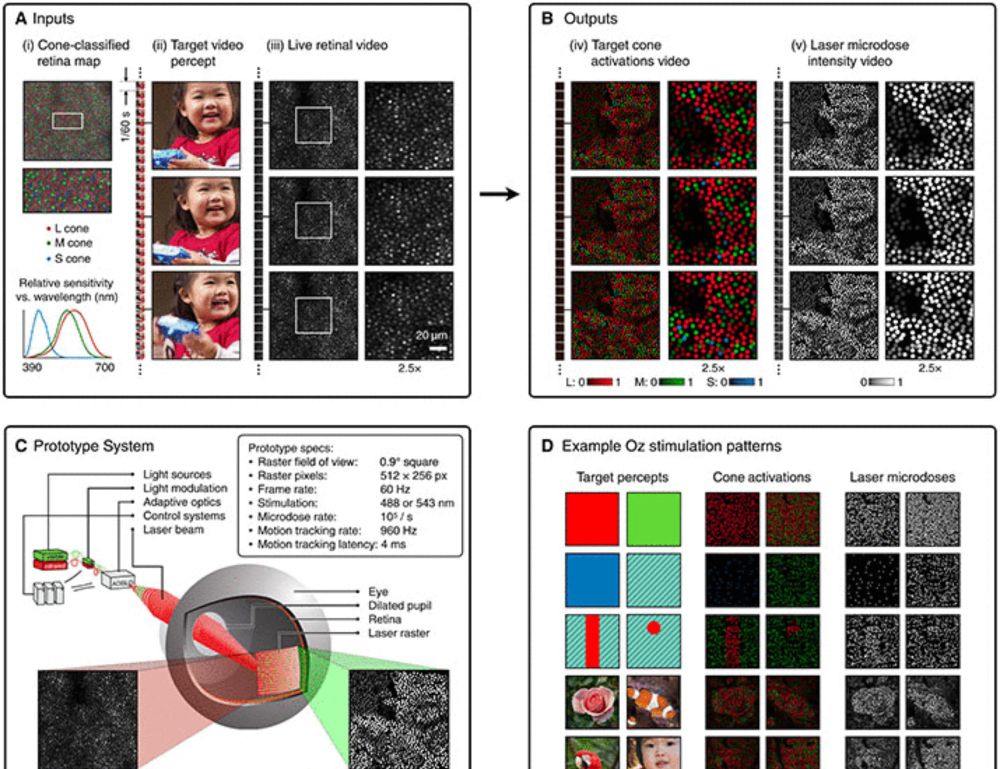
Novel color via stimulation of individual photoreceptors at population scale
Image display by cell-by-cell retina stimulation, enabling colors impossible to see under natural viewing.
scim.ag
April 21, 2025 at 5:56 PM
Five people have seen a color never before visible to the naked human eye, thanks to a new retinal stimulation technique called Oz.
Learn more in #ScienceAdvances: scim.ag/442Hjn6
Learn more in #ScienceAdvances: scim.ag/442Hjn6
Reposted by Chandan Singh
Two clinical trials reported in Nature demonstrate the safety of stem cell therapies for Parkinson’s disease. The papers investigate the use of cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells and human embryonic stem cells. go.nature.com/4ikcJc2
go.nature.com/4jfSRYX 🧪
go.nature.com/4jfSRYX 🧪
April 16, 2025 at 10:18 PM
Two clinical trials reported in Nature demonstrate the safety of stem cell therapies for Parkinson’s disease. The papers investigate the use of cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells and human embryonic stem cells. go.nature.com/4ikcJc2
go.nature.com/4jfSRYX 🧪
go.nature.com/4jfSRYX 🧪
Reposted by Chandan Singh
New preprint! Excited to share our latest work “Accelerated learning of a noninvasive human brain-computer interface via manifold geometry” ft. outstanding former undergraduate Chandra Fincke, @glajoie.bsky.social, @krishnaswamylab.bsky.social, and @wutsaiyale.bsky.social's Nick Turk-Browne 1/8

Accelerated learning of a noninvasive human brain-computer interface via manifold geometry
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) promise to restore and enhance a wide range of human capabilities. However, a barrier to the adoption of BCIs is how long it can take users to learn to control them. W...
doi.org
April 3, 2025 at 11:04 PM
New preprint! Excited to share our latest work “Accelerated learning of a noninvasive human brain-computer interface via manifold geometry” ft. outstanding former undergraduate Chandra Fincke, @glajoie.bsky.social, @krishnaswamylab.bsky.social, and @wutsaiyale.bsky.social's Nick Turk-Browne 1/8
Reposted by Chandan Singh
New preprint “Monkey See, Model Knew: LLMs accurately predict visual responses in humans AND NHPs”
Led by Colin Conwell with @emaliemcmahon.bsky.social Akshay Jagadeesh, Kasper Vinken @amrahs-inolas.bsky.social @jacob-prince.bsky.social George Alvarez @taliakonkle.bsky.social & Marge Livingstone 1/n
Led by Colin Conwell with @emaliemcmahon.bsky.social Akshay Jagadeesh, Kasper Vinken @amrahs-inolas.bsky.social @jacob-prince.bsky.social George Alvarez @taliakonkle.bsky.social & Marge Livingstone 1/n

March 14, 2025 at 4:14 PM
New preprint “Monkey See, Model Knew: LLMs accurately predict visual responses in humans AND NHPs”
Led by Colin Conwell with @emaliemcmahon.bsky.social Akshay Jagadeesh, Kasper Vinken @amrahs-inolas.bsky.social @jacob-prince.bsky.social George Alvarez @taliakonkle.bsky.social & Marge Livingstone 1/n
Led by Colin Conwell with @emaliemcmahon.bsky.social Akshay Jagadeesh, Kasper Vinken @amrahs-inolas.bsky.social @jacob-prince.bsky.social George Alvarez @taliakonkle.bsky.social & Marge Livingstone 1/n
Reposted by Chandan Singh
🚨 New lab paper!🚨
A dream study of mine for nearly 20 yrs not possible until now thanks to NIH 🧠 funding & 1st-author lead @seeber.bsky.social
We tracked hippocampal activity as people walked memory-guided paths & imagined them again. Did brain patterns reappear?🧵👇
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
A dream study of mine for nearly 20 yrs not possible until now thanks to NIH 🧠 funding & 1st-author lead @seeber.bsky.social
We tracked hippocampal activity as people walked memory-guided paths & imagined them again. Did brain patterns reappear?🧵👇
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Human neural dynamics of real-world and imagined navigation - Nature Human Behaviour
Seeber et al. studied brain recordings from implanted electrodes in freely moving humans. Neural dynamics encoded actual and imagined routes similarly, demonstrating parallels between navigational, im...
www.nature.com
March 10, 2025 at 4:52 PM
🚨 New lab paper!🚨
A dream study of mine for nearly 20 yrs not possible until now thanks to NIH 🧠 funding & 1st-author lead @seeber.bsky.social
We tracked hippocampal activity as people walked memory-guided paths & imagined them again. Did brain patterns reappear?🧵👇
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
A dream study of mine for nearly 20 yrs not possible until now thanks to NIH 🧠 funding & 1st-author lead @seeber.bsky.social
We tracked hippocampal activity as people walked memory-guided paths & imagined them again. Did brain patterns reappear?🧵👇
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Reposted by Chandan Singh
2018: Saliency maps give plausible interpretations of random weights, triggering skepticism and catalyzing the mechinterp cultural movement, which now advocates for SAEs.
2025: SAEs give plausible interpretations of random weights, triggering skepticism and ...
2025: SAEs give plausible interpretations of random weights, triggering skepticism and ...


March 3, 2025 at 6:42 PM
2018: Saliency maps give plausible interpretations of random weights, triggering skepticism and catalyzing the mechinterp cultural movement, which now advocates for SAEs.
2025: SAEs give plausible interpretations of random weights, triggering skepticism and ...
2025: SAEs give plausible interpretations of random weights, triggering skepticism and ...
Reposted by Chandan Singh
Yi Ma & colleagues managed to simplify DINO & DINOv2 by removing many ingredients and adding a robust regularization term from information theory (coding rate) that learn informative decorrelated features. Happy to see principled approaches advance deep representation learning!

February 18, 2025 at 2:24 PM
Yi Ma & colleagues managed to simplify DINO & DINOv2 by removing many ingredients and adding a robust regularization term from information theory (coding rate) that learn informative decorrelated features. Happy to see principled approaches advance deep representation learning!
Reposted by Chandan Singh
Can LLMs be used to discover interpretable models of human and animal behavior?🤔
Turns out: yes!
Thrilled to share our latest preprint where we used FunSearch to automatically discover symbolic cognitive models of behavior.
1/12
Turns out: yes!
Thrilled to share our latest preprint where we used FunSearch to automatically discover symbolic cognitive models of behavior.
1/12
February 10, 2025 at 12:21 PM
Can LLMs be used to discover interpretable models of human and animal behavior?🤔
Turns out: yes!
Thrilled to share our latest preprint where we used FunSearch to automatically discover symbolic cognitive models of behavior.
1/12
Turns out: yes!
Thrilled to share our latest preprint where we used FunSearch to automatically discover symbolic cognitive models of behavior.
1/12
Reposted by Chandan Singh
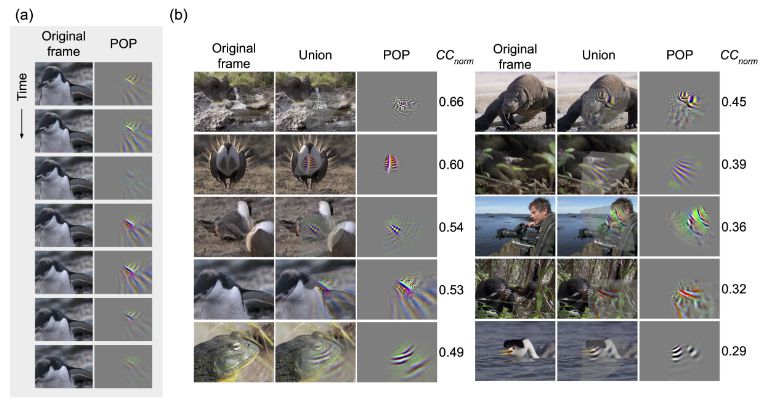
"...responses of V4 neurons under naturalistic conditions can be explained by a hierarchical three-stage model where each stage consists entirely of units like those found in area V1"
#NeuroAI
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
#NeuroAI
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

December 24, 2024 at 8:55 AM
"...responses of V4 neurons under naturalistic conditions can be explained by a hierarchical three-stage model where each stage consists entirely of units like those found in area V1"
#NeuroAI
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
#NeuroAI
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
At NeurIPS this week, presenting our work on crafting *interpretable embeddings* by asking yes/no questions to black-box LLMs.
Drop me a message if you want to chat about interpretability/language neuroscience!
Drop me a message if you want to chat about interpretability/language neuroscience!
December 7, 2024 at 3:05 PM
At NeurIPS this week, presenting our work on crafting *interpretable embeddings* by asking yes/no questions to black-box LLMs.
Drop me a message if you want to chat about interpretability/language neuroscience!
Drop me a message if you want to chat about interpretability/language neuroscience!
Reposted by Chandan Singh
I tried to find everyone who works in the area but I certainly missed some folks so please lmk...
go.bsky.app/BYkRryU
go.bsky.app/BYkRryU
November 23, 2024 at 5:11 AM
I tried to find everyone who works in the area but I certainly missed some folks so please lmk...
go.bsky.app/BYkRryU
go.bsky.app/BYkRryU
Science faces an explainability crisis: ML models can predict many natural phenomena but can't explain them
We tackle this issue in language neuroscience by using LLMs to generate *and validate* explanations with targeted follow-up experiments
We tackle this issue in language neuroscience by using LLMs to generate *and validate* explanations with targeted follow-up experiments

November 20, 2024 at 7:31 PM
Science faces an explainability crisis: ML models can predict many natural phenomena but can't explain them
We tackle this issue in language neuroscience by using LLMs to generate *and validate* explanations with targeted follow-up experiments
We tackle this issue in language neuroscience by using LLMs to generate *and validate* explanations with targeted follow-up experiments
Mechanistic interp has made cool findings but struggled to make them useful
We show that "induction heads" found in LLMs can be reverse-engineered to yield accurate & interpretable next-word prediction models
We show that "induction heads" found in LLMs can be reverse-engineered to yield accurate & interpretable next-word prediction models

November 20, 2024 at 7:28 PM
Mechanistic interp has made cool findings but struggled to make them useful
We show that "induction heads" found in LLMs can be reverse-engineered to yield accurate & interpretable next-word prediction models
We show that "induction heads" found in LLMs can be reverse-engineered to yield accurate & interpretable next-word prediction models

