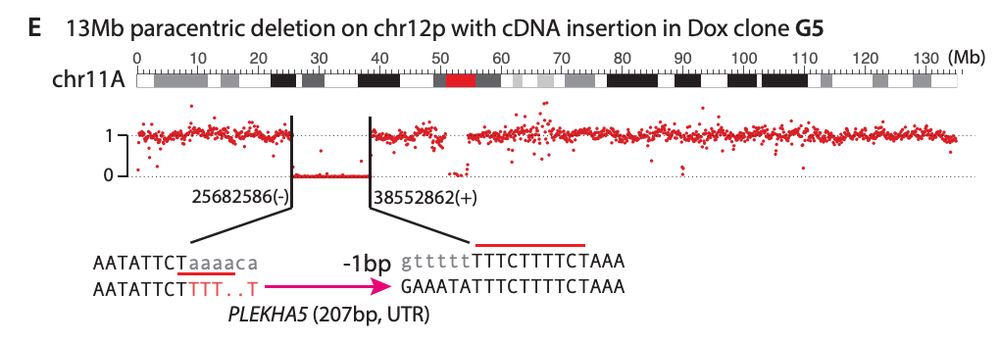
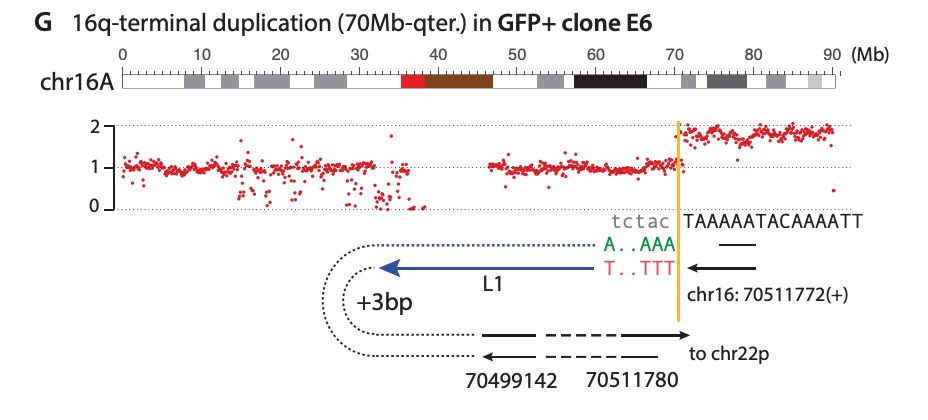
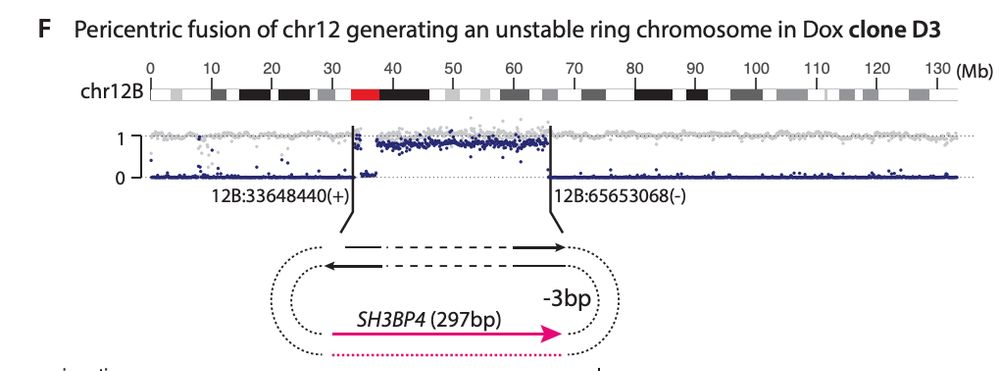
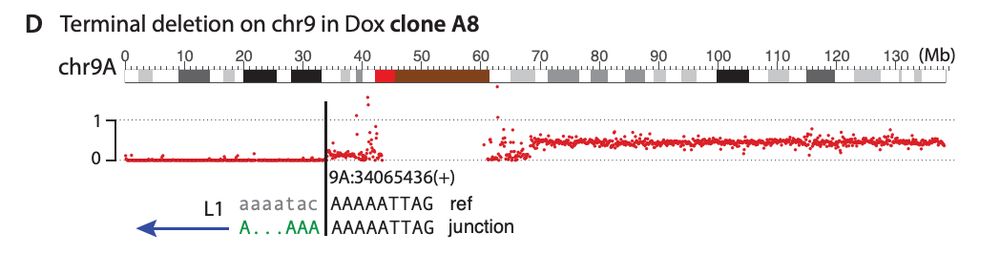
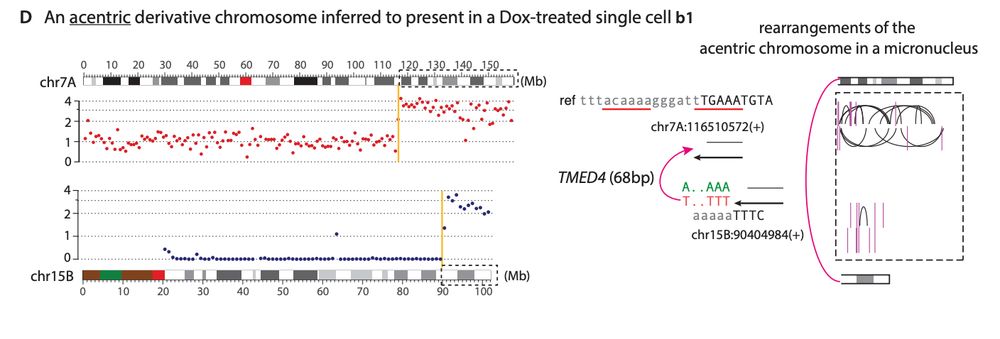
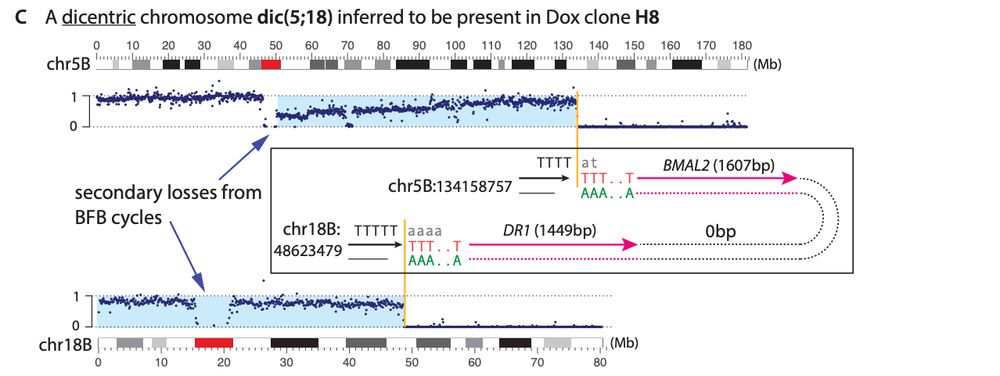
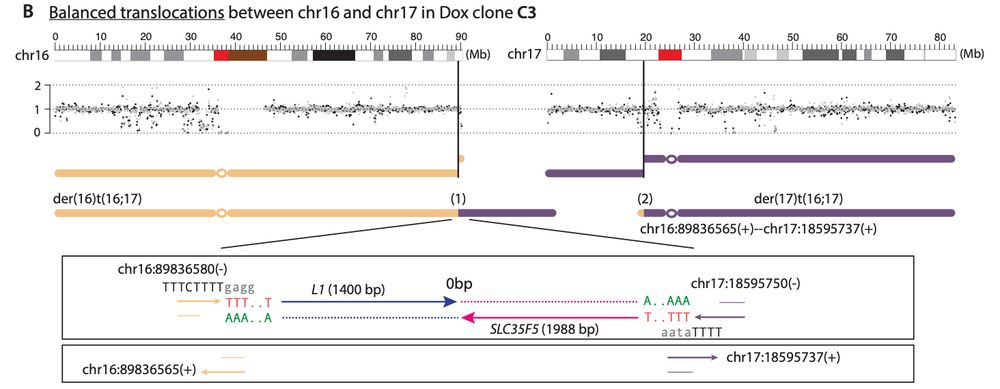
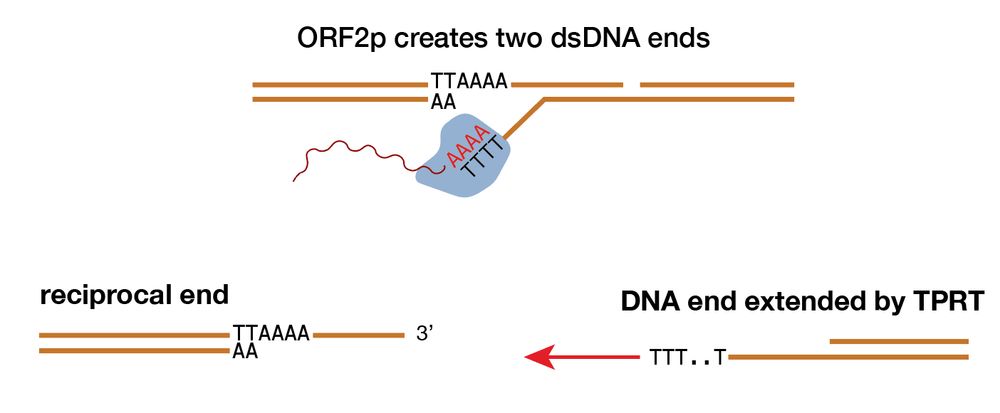
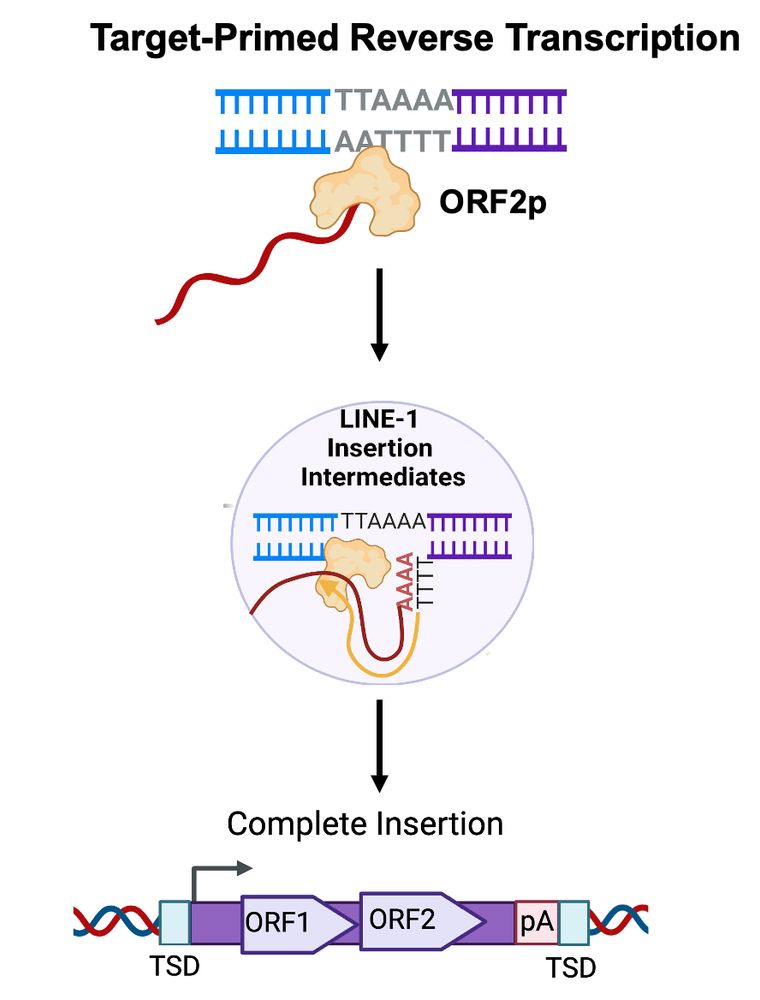
My mentor Dr. Burns established L1 is derepressed in cancers, showing ORF1p detection in malignant tissues and somatic L1 copies in cancer genomes
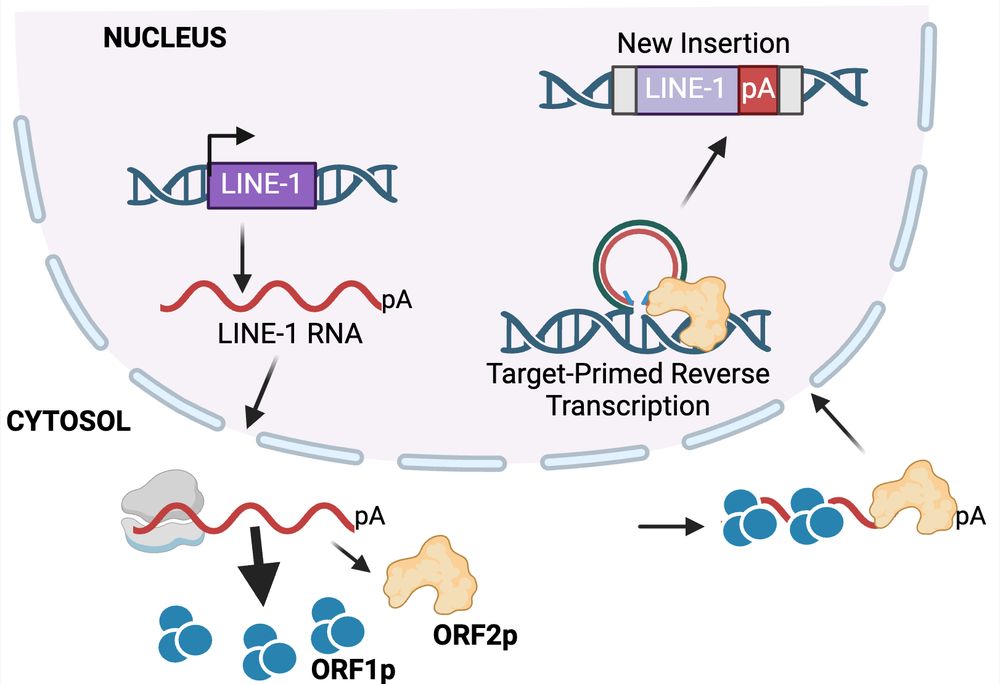
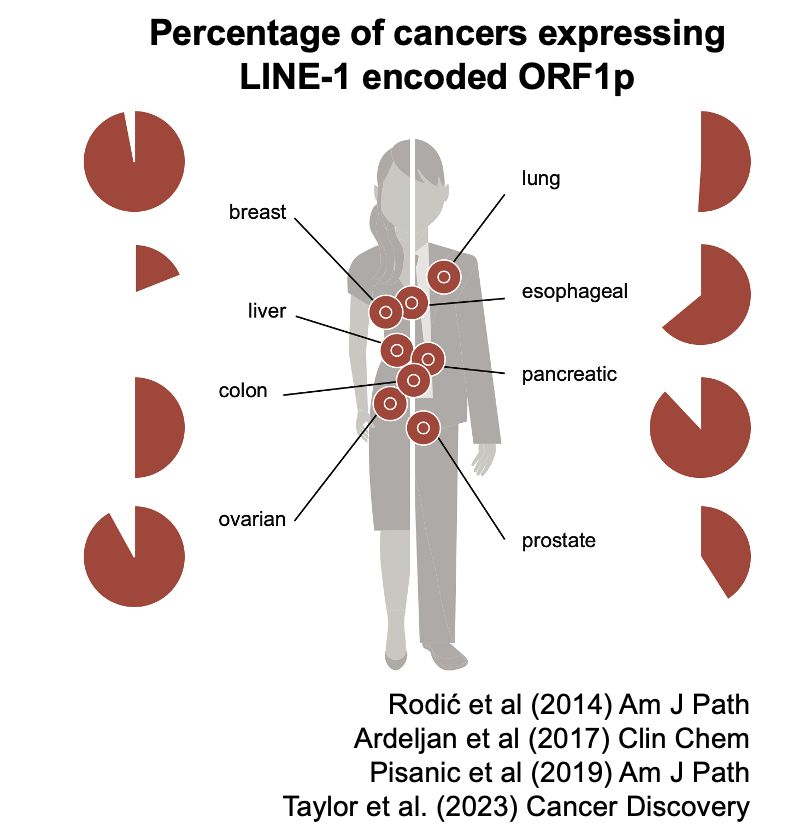
My mentor Dr. Burns established L1 is derepressed in cancers, showing ORF1p detection in malignant tissues and somatic L1 copies in cancer genomes

