ComfyUI-Copilot: An Intelligent Assistant for Automated Workflow Development
An LLM-powered plugin designed to simplify and accelerate workflow creation in ComfyUI, an open-source AI art platform, by providing intelligent node/model recommendations and automated workflow generation.
An LLM-powered plugin designed to simplify and accelerate workflow creation in ComfyUI, an open-source AI art platform, by providing intelligent node/model recommendations and automated workflow generation.

June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
ComfyUI-Copilot: An Intelligent Assistant for Automated Workflow Development
An LLM-powered plugin designed to simplify and accelerate workflow creation in ComfyUI, an open-source AI art platform, by providing intelligent node/model recommendations and automated workflow generation.
An LLM-powered plugin designed to simplify and accelerate workflow creation in ComfyUI, an open-source AI art platform, by providing intelligent node/model recommendations and automated workflow generation.
AReaL: A Large-Scale Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning System for Language Reasoning
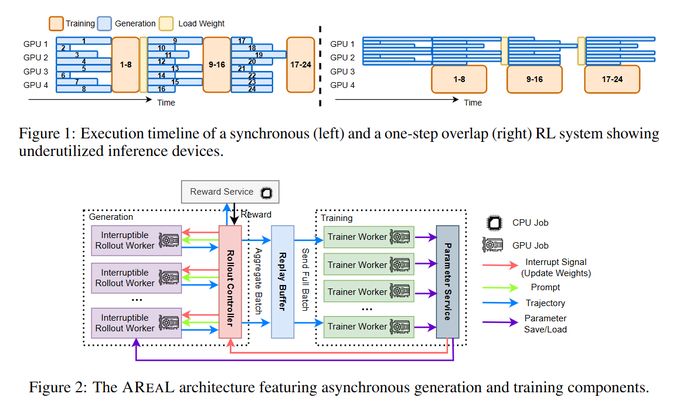
AReaL is an asynchronous reinforcement learning system that efficiently trains large language models for reasoning tasks by maximizing GPU usage and decoupling generation from training.
AReaL is an asynchronous reinforcement learning system that efficiently trains large language models for reasoning tasks by maximizing GPU usage and decoupling generation from training.
June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
AReaL: A Large-Scale Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning System for Language Reasoning
AReaL is an asynchronous reinforcement learning system that efficiently trains large language models for reasoning tasks by maximizing GPU usage and decoupling generation from training.
AReaL is an asynchronous reinforcement learning system that efficiently trains large language models for reasoning tasks by maximizing GPU usage and decoupling generation from training.
Pseudo-Simulation for Autonomous Driving
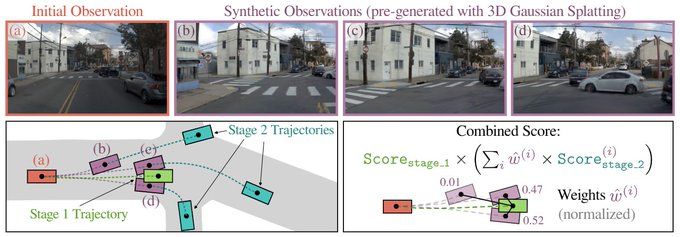
Pseudo-simulation is a new evaluation paradigm for autonomous vehicles that blends the realism of real-world data with the generalization power of simulation, enabling robust, scalable testing without the need for interactive environments.
Pseudo-simulation is a new evaluation paradigm for autonomous vehicles that blends the realism of real-world data with the generalization power of simulation, enabling robust, scalable testing without the need for interactive environments.
June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
Pseudo-Simulation for Autonomous Driving
Pseudo-simulation is a new evaluation paradigm for autonomous vehicles that blends the realism of real-world data with the generalization power of simulation, enabling robust, scalable testing without the need for interactive environments.
Pseudo-simulation is a new evaluation paradigm for autonomous vehicles that blends the realism of real-world data with the generalization power of simulation, enabling robust, scalable testing without the need for interactive environments.
SmolVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Affordable and Efficient Robotics
SmolVLA is a compact, open-source VLA model built for low-cost training and real-world deployment on consumer hardware, enabling efficient language-driven robot control without sacrificing performance.
SmolVLA is a compact, open-source VLA model built for low-cost training and real-world deployment on consumer hardware, enabling efficient language-driven robot control without sacrificing performance.

June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
SmolVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Affordable and Efficient Robotics
SmolVLA is a compact, open-source VLA model built for low-cost training and real-world deployment on consumer hardware, enabling efficient language-driven robot control without sacrificing performance.
SmolVLA is a compact, open-source VLA model built for low-cost training and real-world deployment on consumer hardware, enabling efficient language-driven robot control without sacrificing performance.
ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models
This paper introduces ProRL, a method that uses long-horizon reinforcement learning to unlock new reasoning strategies in LLMs—strategies that base models cannot access, even with extensive sampling.
This paper introduces ProRL, a method that uses long-horizon reinforcement learning to unlock new reasoning strategies in LLMs—strategies that base models cannot access, even with extensive sampling.

June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models
This paper introduces ProRL, a method that uses long-horizon reinforcement learning to unlock new reasoning strategies in LLMs—strategies that base models cannot access, even with extensive sampling.
This paper introduces ProRL, a method that uses long-horizon reinforcement learning to unlock new reasoning strategies in LLMs—strategies that base models cannot access, even with extensive sampling.
The Surprising Effectiveness of Negative Reinforcement in LLM Reasoning
This paper shows that punishing wrong answers—without explicitly rewarding the correct—can be surprisingly effective for improving reasoning in large language models trained via reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards.
This paper shows that punishing wrong answers—without explicitly rewarding the correct—can be surprisingly effective for improving reasoning in large language models trained via reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards.

June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
The Surprising Effectiveness of Negative Reinforcement in LLM Reasoning
This paper shows that punishing wrong answers—without explicitly rewarding the correct—can be surprisingly effective for improving reasoning in large language models trained via reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards.
This paper shows that punishing wrong answers—without explicitly rewarding the correct—can be surprisingly effective for improving reasoning in large language models trained via reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards.
CoT is Not True Reasoning, It Is Just a Tight Constraint to Imitate
This paper challenges the idea that Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting enables true reasoning in LLMs, arguing instead that CoT acts as a structural constraint that guides models to imitate the appearance of reasoning.
This paper challenges the idea that Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting enables true reasoning in LLMs, arguing instead that CoT acts as a structural constraint that guides models to imitate the appearance of reasoning.

June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
CoT is Not True Reasoning, It Is Just a Tight Constraint to Imitate
This paper challenges the idea that Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting enables true reasoning in LLMs, arguing instead that CoT acts as a structural constraint that guides models to imitate the appearance of reasoning.
This paper challenges the idea that Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting enables true reasoning in LLMs, arguing instead that CoT acts as a structural constraint that guides models to imitate the appearance of reasoning.
Why Gradients Rapidly Increase Near the End of Training
This note investigates a sudden rise in gradient norms during the late stages of LLM training and identifies a surprising cause: the interplay between weight decay, normalization layers, and scheduled learning rate decay.
This note investigates a sudden rise in gradient norms during the late stages of LLM training and identifies a surprising cause: the interplay between weight decay, normalization layers, and scheduled learning rate decay.

June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
Why Gradients Rapidly Increase Near the End of Training
This note investigates a sudden rise in gradient norms during the late stages of LLM training and identifies a surprising cause: the interplay between weight decay, normalization layers, and scheduled learning rate decay.
This note investigates a sudden rise in gradient norms during the late stages of LLM training and identifies a surprising cause: the interplay between weight decay, normalization layers, and scheduled learning rate decay.
General agents need world models
This paper proves that any general agent capable of reliably completing diverse, goal-directed tasks must implicitly learn a predictive model of its environment—challenging the notion that model-free learning is sufficient for general intelligence.
This paper proves that any general agent capable of reliably completing diverse, goal-directed tasks must implicitly learn a predictive model of its environment—challenging the notion that model-free learning is sufficient for general intelligence.

June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
General agents need world models
This paper proves that any general agent capable of reliably completing diverse, goal-directed tasks must implicitly learn a predictive model of its environment—challenging the notion that model-free learning is sufficient for general intelligence.
This paper proves that any general agent capable of reliably completing diverse, goal-directed tasks must implicitly learn a predictive model of its environment—challenging the notion that model-free learning is sufficient for general intelligence.
Beyond the 80/20 Rule
This paper investigates how a small subset of high-entropy tokens—termed "forking tokens"—drives the performance of reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) in reasoning tasks for large language models.
This paper investigates how a small subset of high-entropy tokens—termed "forking tokens"—drives the performance of reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) in reasoning tasks for large language models.

June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
Beyond the 80/20 Rule
This paper investigates how a small subset of high-entropy tokens—termed "forking tokens"—drives the performance of reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) in reasoning tasks for large language models.
This paper investigates how a small subset of high-entropy tokens—termed "forking tokens"—drives the performance of reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) in reasoning tasks for large language models.
- Pseudo-Simulation for Autonomous Driving
- AReaL: A Large-Scale Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning System for Language Reasoning
- ComfyUI-Copilot: An Intelligent Assistant for Automated Workflow Development
- AReaL: A Large-Scale Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning System for Language Reasoning
- ComfyUI-Copilot: An Intelligent Assistant for Automated Workflow Development
June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
- Pseudo-Simulation for Autonomous Driving
- AReaL: A Large-Scale Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning System for Language Reasoning
- ComfyUI-Copilot: An Intelligent Assistant for Automated Workflow Development
- AReaL: A Large-Scale Asynchronous Reinforcement Learning System for Language Reasoning
- ComfyUI-Copilot: An Intelligent Assistant for Automated Workflow Development
- The Surprising Effectiveness of Negative Reinforcement in LLM Reasoning
- ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models
- SmolVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Affordable and Efficient Robotics
- ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models
- SmolVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Affordable and Efficient Robotics
June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
- The Surprising Effectiveness of Negative Reinforcement in LLM Reasoning
- ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models
- SmolVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Affordable and Efficient Robotics
- ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models
- SmolVLA: A Vision-Language-Action Model for Affordable and Efficient Robotics
- General agents need world models
- Why Gradients Rapidly Increase Near the End of Training
- CoT is Not True Reasoning, It Is Just a Tight Constraint to Imitate: A Theory Perspective
- Why Gradients Rapidly Increase Near the End of Training
- CoT is Not True Reasoning, It Is Just a Tight Constraint to Imitate: A Theory Perspective
June 10, 2025 at 4:30 PM
- General agents need world models
- Why Gradients Rapidly Increase Near the End of Training
- CoT is Not True Reasoning, It Is Just a Tight Constraint to Imitate: A Theory Perspective
- Why Gradients Rapidly Increase Near the End of Training
- CoT is Not True Reasoning, It Is Just a Tight Constraint to Imitate: A Theory Perspective
HiDream-I1
HiDream-I1 is a 17B-parameter open-source image generation model using a novel sparse Diffusion Transformer (DiT) with dynamic Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to deliver state-of-the-art image quality in seconds while reducing computation.
HiDream-I1 is a 17B-parameter open-source image generation model using a novel sparse Diffusion Transformer (DiT) with dynamic Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to deliver state-of-the-art image quality in seconds while reducing computation.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
HiDream-I1
HiDream-I1 is a 17B-parameter open-source image generation model using a novel sparse Diffusion Transformer (DiT) with dynamic Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to deliver state-of-the-art image quality in seconds while reducing computation.
HiDream-I1 is a 17B-parameter open-source image generation model using a novel sparse Diffusion Transformer (DiT) with dynamic Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to deliver state-of-the-art image quality in seconds while reducing computation.
Silence is Not Consensus
This work introduces the Catfish Agent, a specialized large language model designed to disrupt premature consensus—called Silent Agreement—in multi-agent clinical decision-making systems by injecting structured dissent to improve diagnostic accuracy.
This work introduces the Catfish Agent, a specialized large language model designed to disrupt premature consensus—called Silent Agreement—in multi-agent clinical decision-making systems by injecting structured dissent to improve diagnostic accuracy.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
Silence is Not Consensus
This work introduces the Catfish Agent, a specialized large language model designed to disrupt premature consensus—called Silent Agreement—in multi-agent clinical decision-making systems by injecting structured dissent to improve diagnostic accuracy.
This work introduces the Catfish Agent, a specialized large language model designed to disrupt premature consensus—called Silent Agreement—in multi-agent clinical decision-making systems by injecting structured dissent to improve diagnostic accuracy.
WebDancer: Towards Autonomous Information Seeking Agency
WebDancer is an end-to-end autonomous web agent designed for complex, multi-step information seeking. It combines a data-centric and training-stage pipeline to enable robust reasoning and decision-making in real-world web environments.
WebDancer is an end-to-end autonomous web agent designed for complex, multi-step information seeking. It combines a data-centric and training-stage pipeline to enable robust reasoning and decision-making in real-world web environments.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
WebDancer: Towards Autonomous Information Seeking Agency
WebDancer is an end-to-end autonomous web agent designed for complex, multi-step information seeking. It combines a data-centric and training-stage pipeline to enable robust reasoning and decision-making in real-world web environments.
WebDancer is an end-to-end autonomous web agent designed for complex, multi-step information seeking. It combines a data-centric and training-stage pipeline to enable robust reasoning and decision-making in real-world web environments.
LiteCUA
The authors introduce AIOS 1.0, a platform that helps language models better understand and interact with computers by transforming them into contextual environments. Built on this, LiteCUA is a lightweight agent that uses this structured context to perform digital tasks.
The authors introduce AIOS 1.0, a platform that helps language models better understand and interact with computers by transforming them into contextual environments. Built on this, LiteCUA is a lightweight agent that uses this structured context to perform digital tasks.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
LiteCUA
The authors introduce AIOS 1.0, a platform that helps language models better understand and interact with computers by transforming them into contextual environments. Built on this, LiteCUA is a lightweight agent that uses this structured context to perform digital tasks.
The authors introduce AIOS 1.0, a platform that helps language models better understand and interact with computers by transforming them into contextual environments. Built on this, LiteCUA is a lightweight agent that uses this structured context to perform digital tasks.
Darwin Godel Machine
The Darwin Gödel Machine (DGM) is a self-improving AI system that rewrites its own code to enhance coding performance. Inspired by Gödel machines and Darwinian evolution, it uses empirical validation and an archive of past agents to drive open-ended, recursive improvement.
The Darwin Gödel Machine (DGM) is a self-improving AI system that rewrites its own code to enhance coding performance. Inspired by Gödel machines and Darwinian evolution, it uses empirical validation and an archive of past agents to drive open-ended, recursive improvement.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
Darwin Godel Machine
The Darwin Gödel Machine (DGM) is a self-improving AI system that rewrites its own code to enhance coding performance. Inspired by Gödel machines and Darwinian evolution, it uses empirical validation and an archive of past agents to drive open-ended, recursive improvement.
The Darwin Gödel Machine (DGM) is a self-improving AI system that rewrites its own code to enhance coding performance. Inspired by Gödel machines and Darwinian evolution, it uses empirical validation and an archive of past agents to drive open-ended, recursive improvement.
The Entropy Mechanism of Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning Language Models
This paper analyzes a fundamental barrier in reinforcement learning (RL) for large language models (LLMs): the sharp early collapse of policy entropy, which limits exploration and caps downstream performance.
This paper analyzes a fundamental barrier in reinforcement learning (RL) for large language models (LLMs): the sharp early collapse of policy entropy, which limits exploration and caps downstream performance.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
The Entropy Mechanism of Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning Language Models
This paper analyzes a fundamental barrier in reinforcement learning (RL) for large language models (LLMs): the sharp early collapse of policy entropy, which limits exploration and caps downstream performance.
This paper analyzes a fundamental barrier in reinforcement learning (RL) for large language models (LLMs): the sharp early collapse of policy entropy, which limits exploration and caps downstream performance.
AgriFM
AgriFM is a multi-source temporal remote sensing foundation model tailored for crop mapping. It introduces a modified Video Swin Transformer backbone for unified spatiotemporal processing of satellite imagery from MODIS, Landsat-8/9, and Sentinel-2.
AgriFM is a multi-source temporal remote sensing foundation model tailored for crop mapping. It introduces a modified Video Swin Transformer backbone for unified spatiotemporal processing of satellite imagery from MODIS, Landsat-8/9, and Sentinel-2.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
AgriFM
AgriFM is a multi-source temporal remote sensing foundation model tailored for crop mapping. It introduces a modified Video Swin Transformer backbone for unified spatiotemporal processing of satellite imagery from MODIS, Landsat-8/9, and Sentinel-2.
AgriFM is a multi-source temporal remote sensing foundation model tailored for crop mapping. It introduces a modified Video Swin Transformer backbone for unified spatiotemporal processing of satellite imagery from MODIS, Landsat-8/9, and Sentinel-2.
WorldEval
This paper introduces WorldEval, a real-to-video evaluation framework that uses world models to assess real-world robot manipulation policies in a scalable, safe, and reproducible way. It avoids costly real-world evaluations by simulating robot actions via generated videos.
This paper introduces WorldEval, a real-to-video evaluation framework that uses world models to assess real-world robot manipulation policies in a scalable, safe, and reproducible way. It avoids costly real-world evaluations by simulating robot actions via generated videos.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
WorldEval
This paper introduces WorldEval, a real-to-video evaluation framework that uses world models to assess real-world robot manipulation policies in a scalable, safe, and reproducible way. It avoids costly real-world evaluations by simulating robot actions via generated videos.
This paper introduces WorldEval, a real-to-video evaluation framework that uses world models to assess real-world robot manipulation policies in a scalable, safe, and reproducible way. It avoids costly real-world evaluations by simulating robot actions via generated videos.
Learning to Reason without External Rewards
This paper introduces RLIF, a paradigm where LLMs improve reasoning using intrinsic signals instead of external rewards. The authors propose INTUITOR, which uses a model’s self-confidence—measured as self-certainty—as the sole reward signal.
This paper introduces RLIF, a paradigm where LLMs improve reasoning using intrinsic signals instead of external rewards. The authors propose INTUITOR, which uses a model’s self-confidence—measured as self-certainty—as the sole reward signal.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
Learning to Reason without External Rewards
This paper introduces RLIF, a paradigm where LLMs improve reasoning using intrinsic signals instead of external rewards. The authors propose INTUITOR, which uses a model’s self-confidence—measured as self-certainty—as the sole reward signal.
This paper introduces RLIF, a paradigm where LLMs improve reasoning using intrinsic signals instead of external rewards. The authors propose INTUITOR, which uses a model’s self-confidence—measured as self-certainty—as the sole reward signal.
Paper2Poster
The paper introduces Paper2Poster, the first benchmark for automated academic poster generation, and PosterAgent, a visual-in-the-loop multi-agent system that converts research papers into high-quality posters using open-source models.
The paper introduces Paper2Poster, the first benchmark for automated academic poster generation, and PosterAgent, a visual-in-the-loop multi-agent system that converts research papers into high-quality posters using open-source models.

June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
Paper2Poster
The paper introduces Paper2Poster, the first benchmark for automated academic poster generation, and PosterAgent, a visual-in-the-loop multi-agent system that converts research papers into high-quality posters using open-source models.
The paper introduces Paper2Poster, the first benchmark for automated academic poster generation, and PosterAgent, a visual-in-the-loop multi-agent system that converts research papers into high-quality posters using open-source models.
- WebDancer: Towards Autonomous Information Seeking Agency
- Silence is Not Consensus: Disrupting Agreement Bias in Multi-Agent LLMs via Catfish Agent for Clinical Decision Making
- HiDream-I1: A High-Efficient Image Generative Foundation Model with Sparse Diffusion Transformer
- Silence is Not Consensus: Disrupting Agreement Bias in Multi-Agent LLMs via Catfish Agent for Clinical Decision Making
- HiDream-I1: A High-Efficient Image Generative Foundation Model with Sparse Diffusion Transformer
June 2, 2025 at 4:20 PM
- WebDancer: Towards Autonomous Information Seeking Agency
- Silence is Not Consensus: Disrupting Agreement Bias in Multi-Agent LLMs via Catfish Agent for Clinical Decision Making
- HiDream-I1: A High-Efficient Image Generative Foundation Model with Sparse Diffusion Transformer
- Silence is Not Consensus: Disrupting Agreement Bias in Multi-Agent LLMs via Catfish Agent for Clinical Decision Making
- HiDream-I1: A High-Efficient Image Generative Foundation Model with Sparse Diffusion Transformer

