


🚨 New paper published in RNA!
Scientists often say anecdotally that RNA modifications are disrupted in immortalized cells — but no one’s really tested it.
So we did: ψ-mapping in primary T cells vs. Jurkat cells using direct RNA-seq.
📄 tinyurl.com/TCellPsiRNA
#nanopore #RNA #pseudouridine
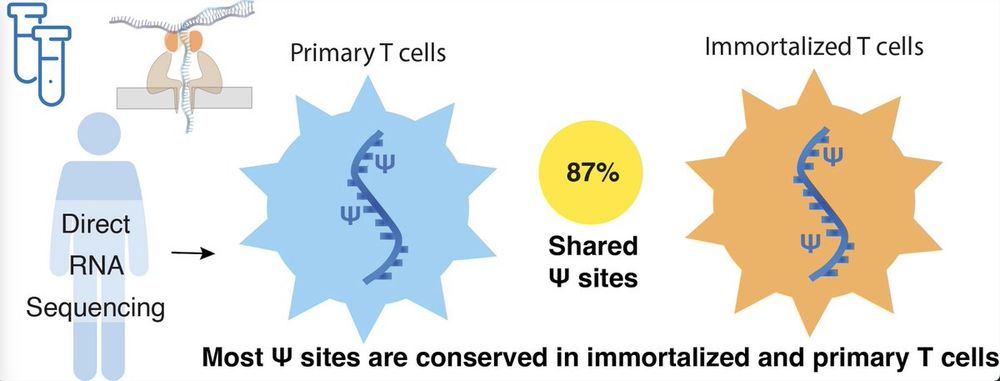
🚨 New paper published in RNA!
Scientists often say anecdotally that RNA modifications are disrupted in immortalized cells — but no one’s really tested it.
So we did: ψ-mapping in primary T cells vs. Jurkat cells using direct RNA-seq.
📄 tinyurl.com/TCellPsiRNA
#nanopore #RNA #pseudouridine
rdcu.be/enfHz
rdcu.be/enfHz
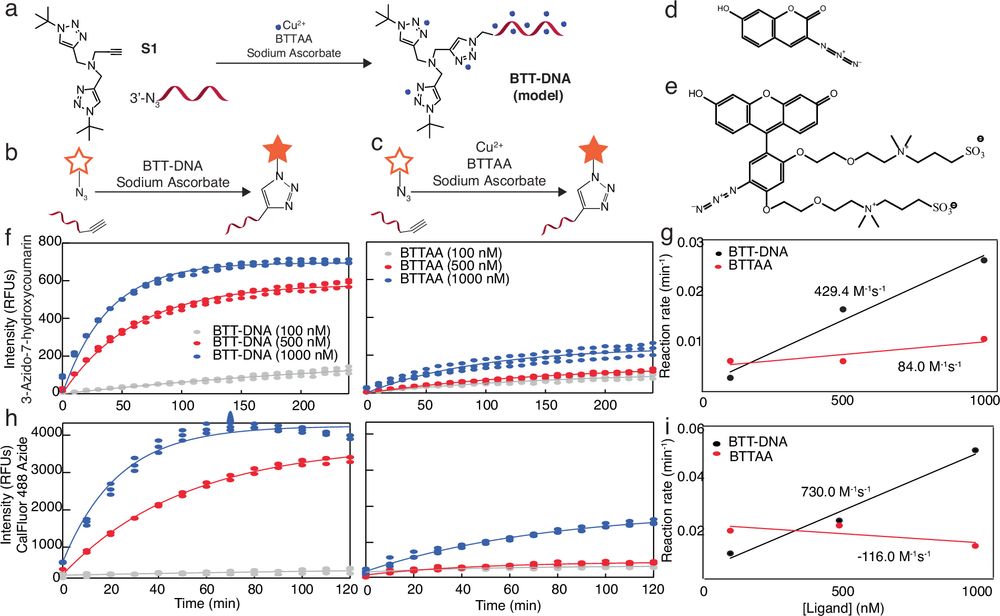
A DNA-conjugated chelator locks Cu⁺ ions for in situ CuAAC at nanomolar doses—zero toxicity.
Read the full paper here ➡️ rdcu.be/enfHz #clickchemistry

A DNA-conjugated chelator locks Cu⁺ ions for in situ CuAAC at nanomolar doses—zero toxicity.
Read the full paper here ➡️ rdcu.be/enfHz #clickchemistry

Do immortalized cells have a different RNA modification profile compared to primary cells? 🤔
@sashafanari.bsky.social @wanunupore.bsky.social @srouhanifard.bsky.social assess the most abundant RNA modification, pseudouridine, in primary and immortalized human T cells
👇
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

Do immortalized cells have a different RNA modification profile compared to primary cells? 🤔
@sashafanari.bsky.social @wanunupore.bsky.social @srouhanifard.bsky.social assess the most abundant RNA modification, pseudouridine, in primary and immortalized human T cells
👇
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
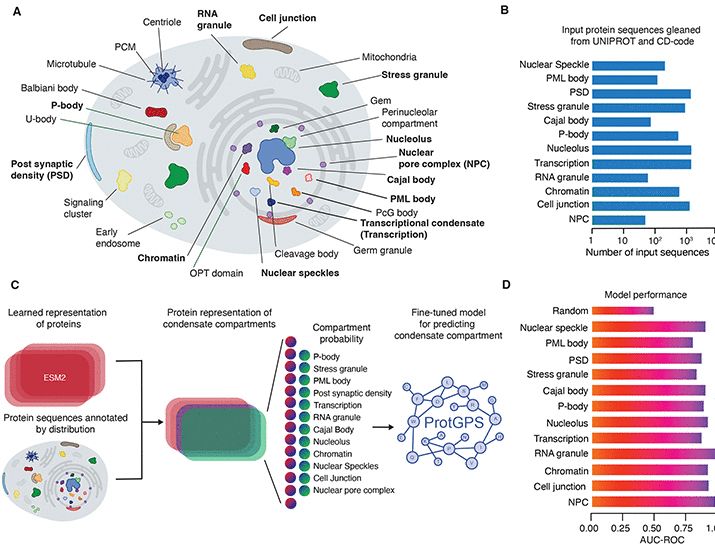
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
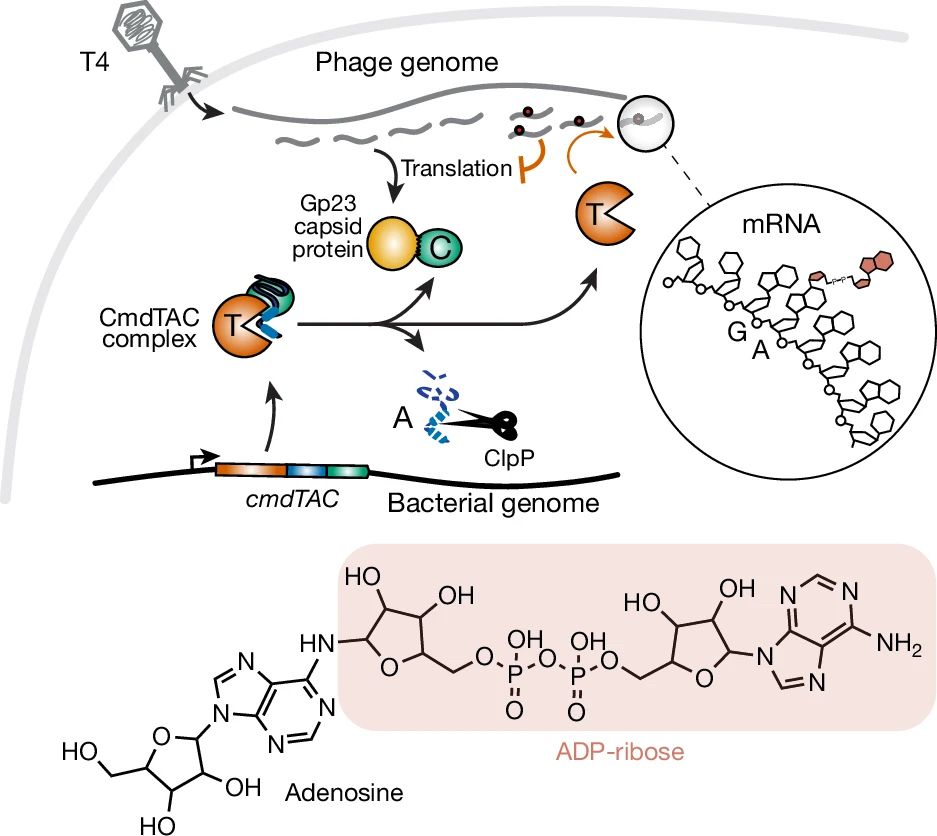
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

