
We examined how people’s eye movements reveal both their predictions and their prediction errors while they watch everyday actions.
👇
We examined how people’s eye movements reveal both their predictions and their prediction errors while they watch everyday actions.
👇

tl;dr: you can now chat with a brain scan 🧠💬
1/n

tl;dr: you can now chat with a brain scan 🧠💬
1/n
A neural state space for episodic memories
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
#neuroskyence #psychscisky #cognition 🧪

A neural state space for episodic memories
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
#neuroskyence #psychscisky #cognition 🧪

downloads.jeffyoshimi.net/NeuralNetwor...




downloads.jeffyoshimi.net/NeuralNetwor...
Entorhinal grid-like codes for visual space during memory formation in @natcomms.nature.com ➡️ rdcu.be/eLRm2
Big thanks to everyone @isabellacwagner.bsky.social, @tobiasstaudigl.bsky.social, @olejensen.bsky.social, @doellerlab.bsky.social, @clauslamm.bsky.social

Entorhinal grid-like codes for visual space during memory formation in @natcomms.nature.com ➡️ rdcu.be/eLRm2
Big thanks to everyone @isabellacwagner.bsky.social, @tobiasstaudigl.bsky.social, @olejensen.bsky.social, @doellerlab.bsky.social, @clauslamm.bsky.social

New paper by @selmalugtmeijer.bsky.social showing that neural states get longer as people age. #PsychSciSky
nature.com/articles/s42003-025-08792-4

New paper by @selmalugtmeijer.bsky.social showing that neural states get longer as people age. #PsychSciSky
nature.com/articles/s42003-025-08792-4


Ever wonder what geom_histogram is actually doing? How about geom_boxplot?
In celebration of the release of #ggplot2 4.0.0 (ggplot8?), I explore the relationships between the “geoms” and “stats” offered by the core {ggplot2} functions.
#rstats

We built an RNN🤖 with key-value episodic memory that learns causal relationships between events and retrieves memories like humans do!
Preprint www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
w/ @qlu.bsky.social, Tan Nguyen &👇

We built an RNN🤖 with key-value episodic memory that learns causal relationships between events and retrieves memories like humans do!
Preprint www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
w/ @qlu.bsky.social, Tan Nguyen &👇
This is a result of an analysis done by a student in my grad seminar, using a large dataset (N=307,313).
What this result might mean: Nobody's personality is truly "average," and people's personality profiles (at least Big 5) might be more "jagged" than we think.
(🧵 1/5)
QUESTION: How many people in this >300K sample do you think fall in the average range for ALL 5 TRAITS?
What's your answer?

This is a result of an analysis done by a student in my grad seminar, using a large dataset (N=307,313).
What this result might mean: Nobody's personality is truly "average," and people's personality profiles (at least Big 5) might be more "jagged" than we think.
(🧵 1/5)
wjschne.github.io/ggdiagram/ar...


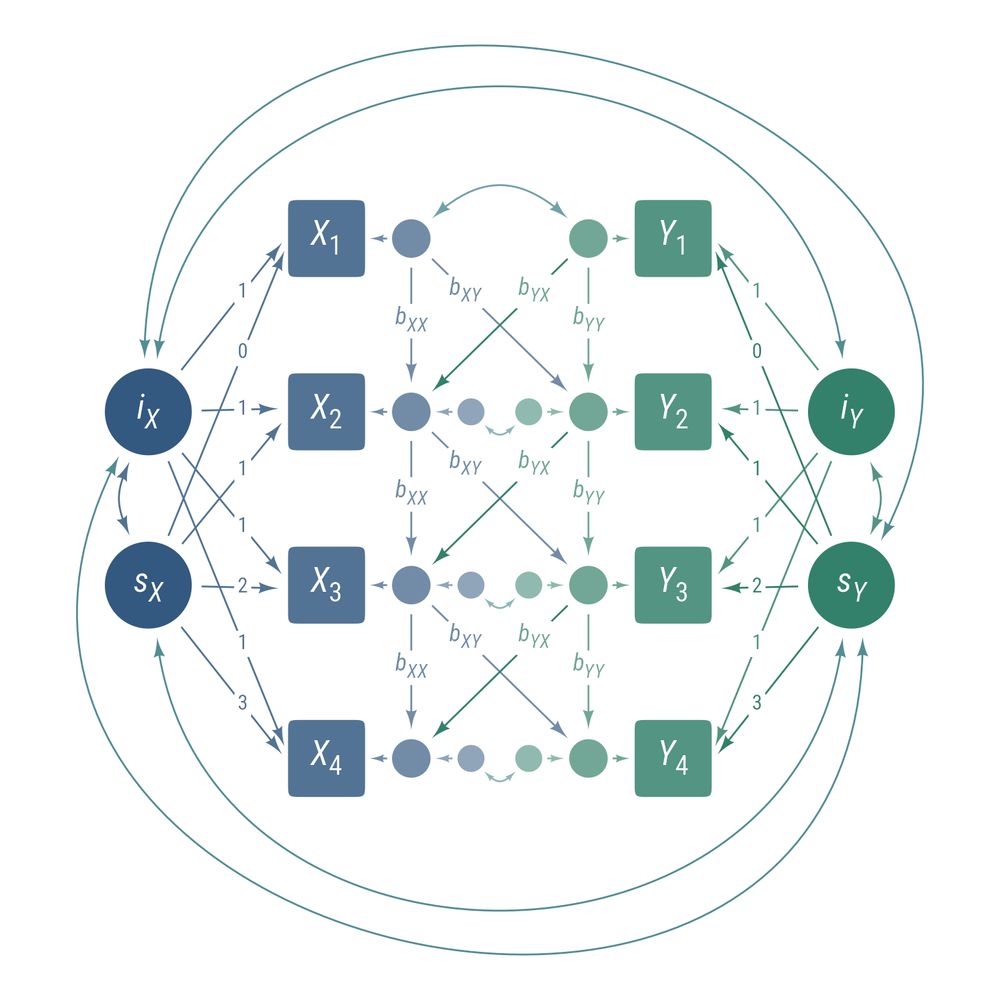

wjschne.github.io/ggdiagram/ar...

Brain regions’ representations can become coarser or finer as event familiarity increases. Fine-tuning predicts memory recall.
Excited to share this work with Narjes Al-Zahli & @chrisbaldassano.bsky.social!

Brain regions’ representations can become coarser or finer as event familiarity increases. Fine-tuning predicts memory recall.
Excited to share this work with Narjes Al-Zahli & @chrisbaldassano.bsky.social!

Cool work by @chrismbird.bsky.social @ayab.bsky.social et al!

Cool work by @chrismbird.bsky.social @ayab.bsky.social et al!

We provide evidence that gaze reinstatement & neural reactivation are deeply related phenomena that jointly reflect the experiences constructed during recall. doi.org/10.1038/s414...
🧵1/9

We provide evidence that gaze reinstatement & neural reactivation are deeply related phenomena that jointly reflect the experiences constructed during recall. doi.org/10.1038/s414...
🧵1/9
Our mind wanders at rest. By periodically probing ongoing thoughts during resting-state fMRI, we show these thoughts are reflected in brain network dynamics and contribute to pervasive links between functional brain architecture and everyday behavior (1/10).
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

Our mind wanders at rest. By periodically probing ongoing thoughts during resting-state fMRI, we show these thoughts are reflected in brain network dynamics and contribute to pervasive links between functional brain architecture and everyday behavior (1/10).
doi.org/10.1101/2025...


