

Great work from Isobel and Alex in my lab @alexlouiseshaw.bsky.social

Great work from Isobel and Alex in my lab @alexlouiseshaw.bsky.social
Read the OA paper in JCB
Read the OA paper in JCB

Huge thanks to Gaelen Guzman, a graduate student/postdoc in the lab who built it from scratch.
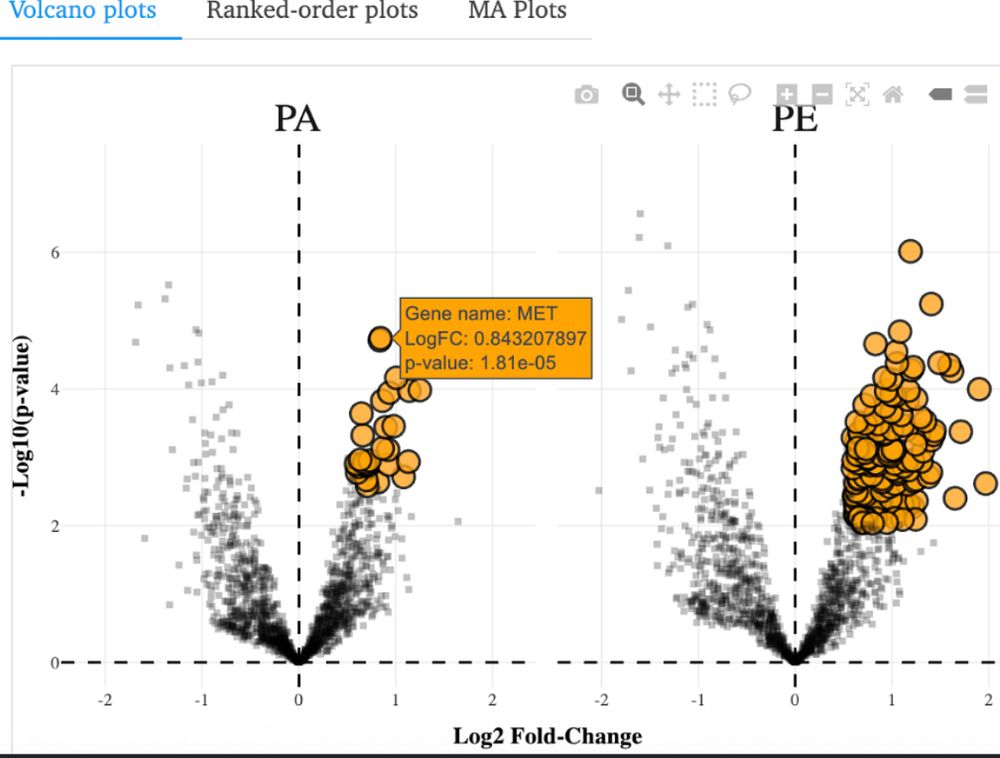
Huge thanks to Gaelen Guzman, a graduate student/postdoc in the lab who built it from scratch.
We highlight recent advances in our understanding of the role the phosphoinositide PIP3 plays in regulating the protein kinases Akt, PDK1, and BTK from a structural perspective.
#kinase #phosphoinositides
portlandpress.com/biochemsoctr...
We highlight recent advances in our understanding of the role the phosphoinositide PIP3 plays in regulating the protein kinases Akt, PDK1, and BTK from a structural perspective.
#kinase #phosphoinositides
portlandpress.com/biochemsoctr...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
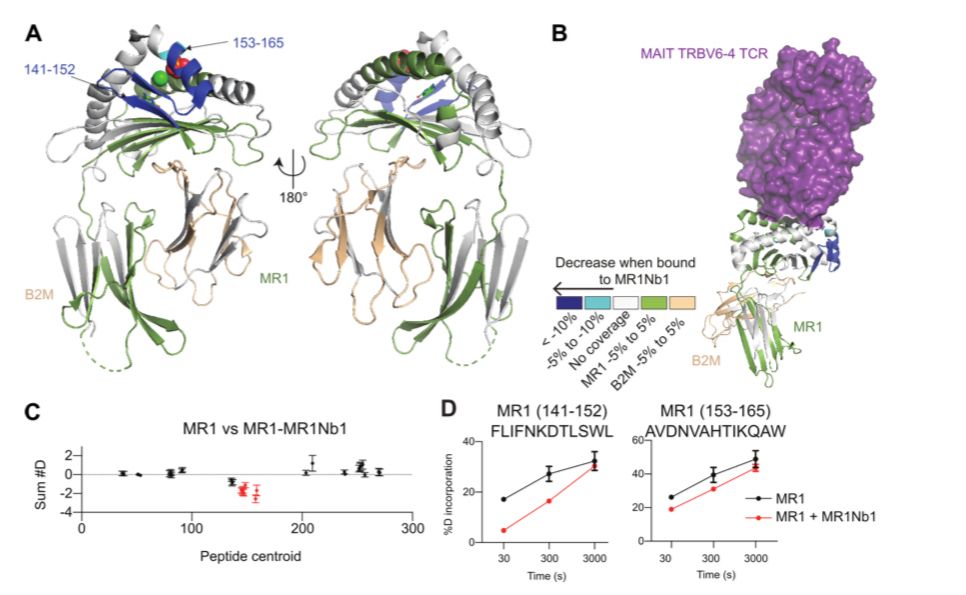
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.ivvy.com.au/event/IUBMB25/
@pseudokinase.bsky.social @iubmb.bsky.social

www.ivvy.com.au/event/IUBMB25/
@pseudokinase.bsky.social @iubmb.bsky.social
www.ivvy.com.au/event/IUBMB25/

www.ivvy.com.au/event/IUBMB25/
chemsymposia.com
chemsymposia.com
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
rupress.org/jcb/article-...

rupress.org/jcb/article-...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
Registration details below
Latest Institute research with special guests ⤵️
www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/cellular-s...

Registration details below
Victoria Holmes and Morgan Ricci led a paper in JCB that answers this question:
rupress.org/jcb/article/...
Read on for a brief thread.

Victoria Holmes and Morgan Ricci led a paper in JCB that answers this question:
rupress.org/jcb/article/...
Read on for a brief thread.
Interested in kinases or pseudokinases? We would love to see you in Queenstown!
www.ivvy.com.au/event/IUBMB2...

Interested in kinases or pseudokinases? We would love to see you in Queenstown!
www.ivvy.com.au/event/IUBMB2...
Fun fact I worked in Dirk Trauner’s lab during my senior year at Berkeley

Fun fact I worked in Dirk Trauner’s lab during my senior year at Berkeley



